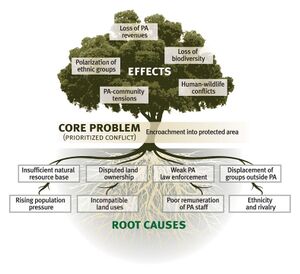
Problem Tree Analysis
A Problem Tree Analysis is a pictorial representation of a problem, its causes and its consequences. This analysis tool helps the project team get a quick glance of how a range of complex issues contribute toward a problem and how this problem branches out into a set of consequences. Both causes and consequences are fitted into the diagram on a hierarchical preference basis.[1]
Problem Tree Analysis (also called Situational Analysis or just Problem Analysis) helps to find solutions by mapping out the anatomy of cause and effect around an issue in a similar way to a Mind map, but with more structure.
Variations of Problem Tree[2]
- Objective Tree: Following the problem tree analysis, it is possible to rephrase each of the problems into positive desirable outcomes – as if the problem had already been treated, the problem can be turned into an objectives tree. In this way, root causes and consequences are turned into root solutions, and key project or influencing entry points are quickly established. A Force Field analysis (Tool 16) could be a useful next step.
- Opportunity Tree: Instead of focusing on ‘problems’ it is possible to use the tree to analyse opportunities. This implies changing the initial question from “what is the problem and what are underlying causes” to “what works well and what are underlying causes”. Can be done after Appreciative story telling (Tool 6).
See Also
Six Thinking Hats
Rätselvermehrung
Brainstorming
Metaplan Method
Mind Mapping
Bisociation
SHARP (Structured, Holistic Approach for a Research Proposal)
References
- ↑ Definition - What Does Problem Tree Analysis Mean? Bright Hub PM
- ↑ Variations of Problem Tree MSP Guide