Difference between revisions of "Risk Assessment"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
A risk assessment is a process to identify potential hazards and analyze what could happen if a hazard occurs. A business impact analysis (BIA) is the process for determining the potential impacts resulting from the interruption of time sensitive or critical business processes.<ref>Defining Risk Assessment [https://www.ready.gov/risk-assessment Ready.Gov]</ref> | A risk assessment is a process to identify potential hazards and analyze what could happen if a hazard occurs. A business impact analysis (BIA) is the process for determining the potential impacts resulting from the interruption of time sensitive or critical business processes.<ref>Defining Risk Assessment [https://www.ready.gov/risk-assessment Ready.Gov]</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Broadly speaking, a risk assessment is the combined effort of: | ||
| + | *identifying and analyzing potential (future) events that may negatively impact individuals, assets, and/or the environment (i.e. risk analysis); and | ||
| + | *making judgments "on the tolerability of the risk on the basis of a risk analysis" while considering influencing factors (i.e. risk evaluation). | ||
| + | Put in simpler terms, a risk assessment determines possible mishaps, their likelihood and consequences, and the tolerances for such events.[1] The results of this process may be expressed in a quantitative or qualitative fashion. Risk assessment is an inherent part of a broader risk management strategy to "introduce control measures to eliminate or reduce" any potential risk-related consequences.<ref>A broad definition of Risk Assessment [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Risk_assessment Wikipedia]</ref> | ||
| Line 11: | Line 16: | ||
*Prioritize hazards and control measures. | *Prioritize hazards and control measures. | ||
*Meet legal requirements where applicable. | *Meet legal requirements where applicable. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
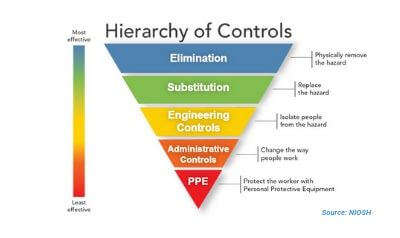
| + | == Implementing Control Measures<ref>How to Implement Control Measures? [https://safetyculture.com/topics/risk-assessment/ iAuditor]</ref> == | ||
| + | After identifying and assigning a risk rating to a hazard, effective controls should be implemented to protect workers. Working through a hierarchy of controls can be an effective method of choosing the right control measure to reduce the risk. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Hierarchy_of_controls.jpg|400px|Hierarchy of controls]]<br /> | ||
| + | source: iAuditor | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | *Eliminate or control all serious hazards immediately. | ||
| + | *Use interim controls while you develop and implement longer-term solutions. | ||
| + | *Select controls according to a hierarchy that emphasizes engineering solutions (including elimination or substitution) first, followed by safe work practices, administrative controls, and finally personal protective equipment. | ||
| + | *Avoid selecting controls that may directly or indirectly introduce new hazards. | ||
| + | *Review and discuss control options with workers to ensure that controls are feasible and effective. | ||
| + | *Use a combination of control options when no single method fully protects workers. | ||
| Line 27: | Line 49: | ||
[[Risk Maturity]]<br /> | [[Risk Maturity]]<br /> | ||
[[Risk Maturity Model (RMM)]]<br /> | [[Risk Maturity Model (RMM)]]<br /> | ||
| − | [[Risk Mitigation]] | + | [[Risk Mitigation]]<br /> |
| + | [[Operational Risk]]<br /> | ||
| + | [[Operational Risk Management (ORM)]]<br /> | ||
| + | [[Architectural Risk]] | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
Revision as of 18:06, 19 March 2020
A risk assessment is a process to identify potential hazards and analyze what could happen if a hazard occurs. A business impact analysis (BIA) is the process for determining the potential impacts resulting from the interruption of time sensitive or critical business processes.[1]
Broadly speaking, a risk assessment is the combined effort of:
- identifying and analyzing potential (future) events that may negatively impact individuals, assets, and/or the environment (i.e. risk analysis); and
- making judgments "on the tolerability of the risk on the basis of a risk analysis" while considering influencing factors (i.e. risk evaluation).
Put in simpler terms, a risk assessment determines possible mishaps, their likelihood and consequences, and the tolerances for such events.[1] The results of this process may be expressed in a quantitative or qualitative fashion. Risk assessment is an inherent part of a broader risk management strategy to "introduce control measures to eliminate or reduce" any potential risk-related consequences.[2]
The Importance of Risk Assessment[3]
Risk assessments are very important as they form an integral part of an occupational health and safety management plan. They help to:
- Create awareness of hazards and risk.
- Identify who may be at risk (e.g., employees, cleaners, visitors, contractors, the public, etc.).
- Determine whether a control program is required for a particular hazard.
- Determine if existing control measures are adequate or if more should be done.
- Prevent injuries or illnesses, especially when done at the design or planning stage.
- Prioritize hazards and control measures.
- Meet legal requirements where applicable.
Implementing Control Measures[4]
After identifying and assigning a risk rating to a hazard, effective controls should be implemented to protect workers. Working through a hierarchy of controls can be an effective method of choosing the right control measure to reduce the risk.
- Eliminate or control all serious hazards immediately.
- Use interim controls while you develop and implement longer-term solutions.
- Select controls according to a hierarchy that emphasizes engineering solutions (including elimination or substitution) first, followed by safe work practices, administrative controls, and finally personal protective equipment.
- Avoid selecting controls that may directly or indirectly introduce new hazards.
- Review and discuss control options with workers to ensure that controls are feasible and effective.
- Use a combination of control options when no single method fully protects workers.
See Also
Risk Analysis
Risk Assessment Framework (RAF)
Risk Management
Risk Management Framework (RMF)
Information Technology Risk (IT Risk)
Enterprise Risk Management (ERM)
Risk IT Framework
Risk Based Testing
Risk-Adjusted Return
Risk-Adjusted Return on Capital (RAROC)
Risk Matrix
Risk Maturity
Risk Maturity Model (RMM)
Risk Mitigation
Operational Risk
Operational Risk Management (ORM)
Architectural Risk