Difference between revisions of "Transactional Leadership"
(Transactional Leadership is a leadership that maintains or continues the status quo. It is also the leadership that involves an exchange process, whereby followers get immediate, tangible rewards for carrying out the leader’s orders.) |
|||
| (4 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | Transactional Leadership is a | + | == What is Transactional Leadership? == |
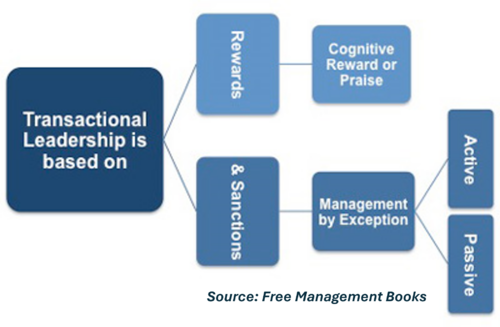
| + | '''Transactional leadership''' is a management style that focuses on the exchange between leaders and followers. It is based on a system of rewards and penalties for performance. This leadership style assumes that employees are motivated by reward and punishment and work best under a clear chain of command. Transactional leaders emphasize order and structure; they are often highly directive and operate through a formal task and reward alignment system. | ||
| − | |||
| + | [[File:Transactional Leadership.png|500px|Transactional Leadership]] | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | __TOC__ | ||
| − | ===References | + | |
| + | == Role and Purpose of Transactional Leadership == | ||
| + | The primary role of transactional leadership is to maintain regular operations and achieve goals efficiently by managing the team's performance through a series of transactions. The purposes include: | ||
| + | *Directing Behavior: Using rewards and punishments to influence employee actions and decisions. | ||
| + | *Maintaining Routine: Ensuring operations run smoothly by adhering to established processes and guidelines. | ||
| + | *Achieving Specific Objectives: Focusing on clear short-term goals requiring high oversight and coordination. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | == Usage of Transactional Leadership == | ||
| + | Transactional leadership is particularly effective in: | ||
| + | *Crisis Management: Where quick, decisive action is needed, and the scope for error is minimal. | ||
| + | *Regulated Industries: In environments like manufacturing or finance where precision, safety, and adherence to rules are paramount. | ||
| + | *Routine Operations: Where tasks are repetitive and require a consistent level of performance. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | == Importance of Transactional Leadership == | ||
| + | Transactional leadership is important because it: | ||
| + | *Provides Clear Structure: The clear expectations and rewards system helps maintain discipline and operational consistency. | ||
| + | *Efficiently Motivates Performance: Effective for motivating employees to perform at expected levels and meeting organizational goals. | ||
| + | *Facilitates Stability: Helps maintain order and efficiency in organizations with well-established routines and methods. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | == Benefits of Transactional Leadership == | ||
| + | Implementing transactional leadership offers several advantages: | ||
| + | *Predictability: High level of predictability in management and operations. | ||
| + | *Straightforward Metrics for Performance: Clear benchmarks for success and failure can simplify performance evaluations. | ||
| + | *Quick Results: Often results in quick outcomes as it is focused on immediate tasks and specific objectives. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | == Examples of Transactional Leadership in Practice == | ||
| + | *Sales Teams: Where leaders offer commissions or bonuses based on performance metrics. | ||
| + | *Customer Service Departments: Leaders incentivize employees to handle a certain number of calls or maintain customer satisfaction scores. | ||
| + | *Production Lines: Supervisors ensure that employees adhere to productivity and safety standards, with rewards tied to exceeding targets and penalties for non-compliance. | ||
| + | *Transactional leadership remains a popular and effective leadership style in environments where tasks are clear-cut, and goals are oriented towards efficiency and productivity. While it may not foster innovation or personal growth as strongly as other leadership styles, it can effectively optimize processes and achieve predictable, solid performance across many sectors. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | == See Also == | ||
| + | *[[Leadership Styles]]: Providing an overview of different leadership styles, including transformational and democratic leadership, to contrast with transactional leadership and illustrate different approaches to management and motivation. | ||
| + | *[[Performance Management]]: Discussing how transactional leadership applies to performance management, emphasizing clear structures and measurable goals to evaluate employee performance. | ||
| + | *[[Organizational Behavior]]: Linking to how transactional leadership influences organizational behavior, particularly regarding employee motivation and job satisfaction. | ||
| + | *[[Change Management]]: Explaining the strengths and limitations of transactional leadership in managing change, particularly its effectiveness in stable environments versus dynamic ones. | ||
| + | *[[Conflict Resolution]]: Covering the role of transactional leaders in conflict resolution, often focusing on resolving issues quickly to maintain a steady workflow. | ||
| + | *[[Human Resource Management (HRM)]]: Exploring how transactional leadership integrates with human resource practices, particularly in recruitment, training, and compensation strategies. | ||
| + | *[[Team Dynamics]]: Discussing the effect of transactional leadership on team dynamics, including how it may foster dependency on the leader for direction and rewards. | ||
| + | *[[Business Strategy]]: Linking transactional leadership to business strategy execution, particularly in how it can effectively implement short-term objectives and operational goals. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | == References == | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
Latest revision as of 19:44, 9 May 2024
What is Transactional Leadership?
Transactional leadership is a management style that focuses on the exchange between leaders and followers. It is based on a system of rewards and penalties for performance. This leadership style assumes that employees are motivated by reward and punishment and work best under a clear chain of command. Transactional leaders emphasize order and structure; they are often highly directive and operate through a formal task and reward alignment system.
Role and Purpose of Transactional Leadership
The primary role of transactional leadership is to maintain regular operations and achieve goals efficiently by managing the team's performance through a series of transactions. The purposes include:
- Directing Behavior: Using rewards and punishments to influence employee actions and decisions.
- Maintaining Routine: Ensuring operations run smoothly by adhering to established processes and guidelines.
- Achieving Specific Objectives: Focusing on clear short-term goals requiring high oversight and coordination.
Usage of Transactional Leadership
Transactional leadership is particularly effective in:
- Crisis Management: Where quick, decisive action is needed, and the scope for error is minimal.
- Regulated Industries: In environments like manufacturing or finance where precision, safety, and adherence to rules are paramount.
- Routine Operations: Where tasks are repetitive and require a consistent level of performance.
Importance of Transactional Leadership
Transactional leadership is important because it:
- Provides Clear Structure: The clear expectations and rewards system helps maintain discipline and operational consistency.
- Efficiently Motivates Performance: Effective for motivating employees to perform at expected levels and meeting organizational goals.
- Facilitates Stability: Helps maintain order and efficiency in organizations with well-established routines and methods.
Benefits of Transactional Leadership
Implementing transactional leadership offers several advantages:
- Predictability: High level of predictability in management and operations.
- Straightforward Metrics for Performance: Clear benchmarks for success and failure can simplify performance evaluations.
- Quick Results: Often results in quick outcomes as it is focused on immediate tasks and specific objectives.
Examples of Transactional Leadership in Practice
- Sales Teams: Where leaders offer commissions or bonuses based on performance metrics.
- Customer Service Departments: Leaders incentivize employees to handle a certain number of calls or maintain customer satisfaction scores.
- Production Lines: Supervisors ensure that employees adhere to productivity and safety standards, with rewards tied to exceeding targets and penalties for non-compliance.
- Transactional leadership remains a popular and effective leadership style in environments where tasks are clear-cut, and goals are oriented towards efficiency and productivity. While it may not foster innovation or personal growth as strongly as other leadership styles, it can effectively optimize processes and achieve predictable, solid performance across many sectors.
See Also
- Leadership Styles: Providing an overview of different leadership styles, including transformational and democratic leadership, to contrast with transactional leadership and illustrate different approaches to management and motivation.
- Performance Management: Discussing how transactional leadership applies to performance management, emphasizing clear structures and measurable goals to evaluate employee performance.
- Organizational Behavior: Linking to how transactional leadership influences organizational behavior, particularly regarding employee motivation and job satisfaction.
- Change Management: Explaining the strengths and limitations of transactional leadership in managing change, particularly its effectiveness in stable environments versus dynamic ones.
- Conflict Resolution: Covering the role of transactional leaders in conflict resolution, often focusing on resolving issues quickly to maintain a steady workflow.
- Human Resource Management (HRM): Exploring how transactional leadership integrates with human resource practices, particularly in recruitment, training, and compensation strategies.
- Team Dynamics: Discussing the effect of transactional leadership on team dynamics, including how it may foster dependency on the leader for direction and rewards.
- Business Strategy: Linking transactional leadership to business strategy execution, particularly in how it can effectively implement short-term objectives and operational goals.