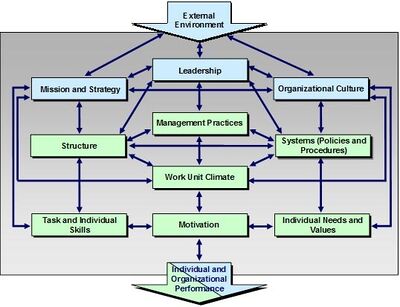
Burke-Litwin Model of Organizational Performance and Change
Burke-Litwin is a system science model that describes the linkages among the key factors that affect performance, and determine how change occurs in an organization. Through the use of this model system, engineers obtain data on what organizational factors to change and why. Higher level factors (blue boxes) have greater weight in effecting organizational change; a change in any variable will ultimately affect every other variable. The Figure below, Burke-Litwin Model of Organizational Performance and Change, depicts the system science approach:
This Performance and Change Model, developed in 1992 by two organizational change consultants, W. Warmer Burke and George H. Litwin, is a tool used to understand an organization's component parts and how they relate to each other in a time of change. A common reason for a change initiative failing is all areas of the organization affected by the change are not accounted for. Therefore, using this model can reveal what areas of the business are affected and how they are interrelated. The model also demonstrates the hierarchy of factors within an organization and hence the flow of influence from one factor to the next. The model is an example of ‘open systems theory’, which suggests change comes from external influences. The authors describe the model as a mechanism that portrays “…the primary variables that need to be considered in any attempt to predict and explain the total behavior output of an organization, the most important interactions between these variables, and how they affect change”. There are four groups of elements within an organization; the external environment, transformational factors, transactional factors and performance. Each group then contains various elements of the organization. The diagram above demonstrates which elements belong in which group, how they interact with each other and the overall hierarchy of an organization.[1]
Burke-Litwin Model - The Three Levels of Change
This Burke-Litwin Model identifies three levels of changes in an organization which are derived by 12 factors or drivers of change.
- Transformational Change: Transformational factors are deeply embedded processes and characteristics of the organization. Any change that occurs to these factors will have substantial consequences to the rest of the organization. It is also true that any other change will require these factors’ input and hence the arrows go in both directions. Lasting change to any of these factors is likely to sweep change throughout the organization. These factors will be most strongly affected by the external environment and will also have the strongest influence on transactional factors.
- Transactional Change: Transactional factors refer to day-to-day operations within the organization. The authors argue these factors are strongly affected by management, rather than leadership. Change in these factors is only likely to lead to lasting change if, in turn, the transformational factors are also affected.
- Individual and Organizational Performance – This factor is the overall output of the organization. This can be represented in many different ways, commonly turnover, productivity, customer satisfaction etc.
The Burke-Litwin model - Drivers of Change
Burke-Litwin believe environmental factors to be the most important driver for change. Indeed, most change can be traced back to external drivers for change. Important elements of organizational success, such as mission and strategy, leadership and organizational culture, are often impacted by changes that originate outside the organization.
- The external environment, including market, legislation, competition and economic factors. All of this has an impact on the organization, and as a change manager, you must constantly review the environment of issues that affect you and your team.
- Mission and strategy - The mission of an organization defines its reason for existence. It is the basis of all activities. Then, the strategy explains in a broad sense how the organization will accomplish its mission. Usually, the strategy will change according to the situation and will have a significant impact on your work. As a change manager, you need to understand strategic changes and be able to communicate their impact to employees.
- Leadership-This takes into account the attitudes and behaviors of senior colleagues and how the entire organization sees these behaviors. The way in which change is achieved and accepted through the organization will be severely affected by the top team. Does your team believe that senior colleagues will commit to change, or is this just another initiative that will disappear in six months?
- Organizational culture - It takes into account the beliefs, behaviors, values and practices that prevail in the organization. Cultural change is not an overnight event. It has evolved over time due to many other changes in the organization. As a manager, you should keep in mind the ideal state of the organization, how people are expected to behave (or not to behave), and what your organization values.
- Structure - Changes in strategy often lead to changes in organizational structure. This affects relationships, responsibilities, and work styles. Your job is to assess the impact of structural changes and make sure that your team understands why structural changes are needed and what it means to them.
- Management practices - what are the actions and procedures that managers take to put the plan into place. Managers, leaders, and staff are taught how to follow rules and regulations, as well as the essence of relationships between ranks and units, through these activities.
- Workplace environment-This takes into account the employees’ perceptions of their direct colleagues and the work environment. Our immediate work environment often shapes our perception of the entire organization and affects our job satisfaction. The changes in the immediate work environment need to be managed sensitively, because they may trigger a series of emotional and political reactions from the staff. This is especially true if the change involves moving locations, changing personnel, or changing service conditions (such as working hours).
- The working atmosphere - refers to the organizational environment; how the employees' attitudes toward work are; whether they are satisfied with the organizational culture; how do they feel about the leadership.
- Task requirements and individual skills - Higher-level changes in the organization often require changes in the work performed and the skills available to the team. As a change manager, you need to evaluate whether: all the right skills are in place: can they be developed: or whether these skills need to be introduced from outside the team.
- Individual needs and values - Team dynamics can change as a result of changes in team membership. We would be able to hire appropriate talents for our team in terms of personal appearance, abilities, and expertise in an ideal future. In practice, however, this is not always possible. Your job is to detect and minimize any threats in this area as much as possible.
- Employee Motivation - The motivation of employees takes into account the importance of personal and organizational goals. Incentives are the key to effective change. The real challenge is to maintain momentum throughout the change project, especially when the change is often not accepted by those affected.
- Individual and organizational performance – Individual performance relates to the ability to achieve targets in a timely and successful way. Individual success adds up to corporate performance. The achievement of business objectives over time serves as the benchmark for measuring organizational success.
Pros and Cons of Burke-Litwin Model[2]
Advantages of Burke Litwin Model of Change.
- This is a comprehensive model covers all the important factors into account to explain why change is happening, what is driving change and helps in formulating change strategy.
- This model explains factors of change on the basis of cause and effect relationship which helps to have complete understanding about organizational change.
- This model explains the meaning and distinction between transformational and transactional level of change leadership in an organization.
Limitations and Disadvantages of Burke Litwin Model of Change
- The critics of this model are of the view that over simplification of different factors of change results into producing sub factors which actually makes it a more complex model.
- This model only focuses on what drives change and fail to explain how to implement change.
- It puts external environment factors on the top which drives change which is not always the case. There are internal factor as powerful factors which lead to organizational change.
=See Also
- Organizational Performance
- Organizational Change
- Organizational Change Management (OCM)
- Causal Model of Organizational Performance and Change
- Change Management
- Congruence Model
References
- ↑ Explaining the Burke-Litwin Model Accipio
- ↑ Pros and Cons of Burke-Litwin Model Change Management Insight