Business Process Integration
Business Process Integration (BPI) is the synchronization of a company’s internal operations with those of its other divisions and its trading partners by connecting disparate systems in real-time.[1]
BPI allows for automation of business processes, integration of systems and services, and the secure sharing of data across numerous applications. Overcoming integration challenges allows organizations to connect systems internally and externally. Moreover, BPI allows for the automation of management, operational, and supporting processes. This gives businesses an edge over competitors as they can spend less time concerned about the challenges of integration and more time and energy on driving new business. Previously, business process integration software was only available to large enterprise companies that could afford it. Today, businesses of all sizes need a efficient integration solution to streamline processes between marketing, sales, customer service, and supply chain management, etc. Integration among administrative, operational, and support processes increases productivity by simplifying regular enterprise functions.[2]
The primary problem with business process integration lies in how a business process embedded in one application is being bridged into the process of another. The business processes linked together are described in terms of activities or Workflows and bring human Actors as a distinguishing element of the solution. BPI solutions allow enterprises to take advantage of systems that are already in place by automating and managing the business processes that span these systems. With BPI, enterprises can preserve major investments in legacy systems thereby avoiding the expense of having to write additional code to replicate existing functionality. [Papazoglou Ribbers, 2006][3]
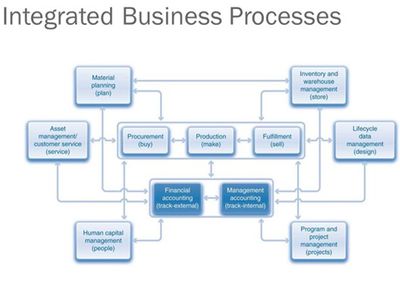
source: Simha R, Magal
Business Process Integration Software[4]
An effective business integration process model should help organizations with the following issues:
- Process Gaps: Business Process Management (BPM) integration reduces delays or errors.
- Needless Duplication: Business process integration avoids duplication that wastes resources and may result in data inconsistencies.
- Disparate Processes: Gain a better understanding of how different processes impact each other. Essential knowledge in support of business process improvement programs.
- Real-Time Visibility: Essential to effective business performance management programs.
Types of Business Process Integration (BPI)[5]
There are 3 different types of business process integrations:
- Process Trigger – Event happening in a certain system triggers a process in your BPM, as with the onboarding example.
- Pull – The data is automatically transferred from any given system to the BPM, allowing for participants in the process to make use of it.
- Push – Transferring the data from the BPM to a different system. So for example, if the process in question is hiring, it could be the transfer of the successful candidate’s data to the HRM system.
Steps to a Successful Business Process Integration[6]
- Process Identification: In order to implement BPI, processes must first be identified. A good way to do this is by using business process mapping (BPM) tools. These tools use words and visual layouts to demonstrate typical functions. Because more organizations are seeking ways to map business processes, a number of BPM tools have been created to make it easier and faster. The most popular tool is process mapping software, which provides a good indicator of the organization’s ability to document existing processes and prove that they are effective in achieving the goals of the business. BPM software can also provide process modeling, which offers real-time insight into how any proposed adjustments could affect existing processes and, hence, the overall business function. BPM software can also help automate existing processes and incorporate them across various parts of the business. Mapping tools can also help businesses comply with industry regulations such as ISO 9000, which often requires documentation of quality system processes.
- Documenting and Mapping: The first step in BPM is to document an organization's existing business processes. BPM tools provide the ability to create flow charts and other visual tools that show these existing processes and their relationships to one another. After processes have been documented, they can be evaluated and reviewed to make sure they sufficiently outline the real-time activities of the organization. Process mapping also makes it easier to pinpoint inefficiencies and areas for improvement within processes. Organizations also may use BPM tools to automate existing functions, increasing effectiveness and consistency across different departments within the business. Software can help the systems of different departments communicate with each other and share required information. Process automation often saves time and money and can help businesses implement uniform workflow processes across all areas of the company. This is especially true for companies that have regulatory requirements and are expected to document their processes and guarantee compliance.
- Planning Through Modeling: In the next step, resellers can help their clients create models of the processes that have been mapped out to illustrate the proposed changes to the system to be hypothetically implemented. This allows process owners to see the possible outcomes of a change and to be able to assess if it adequately zones in on the inefficiencies that may have been identified in the first steps. Process simulations allow proposed changes to be implemented in theory and their effects observed and assessed before actual changes are made.
- Design, Implementation, and Management: The design and implementation of BPI help eliminate the need to duplicate data in different systems and increase the comprehensive efficiency of the business’s operation. When designed and implemented properly, BPI can save companies time and money. An example of BPI could involve initiating a relationship between the sales and billing systems within a company. In some cases, the connection is reciprocal, meaning that specific data within the sales database can be accessed by the billing system and vice versa. This means that if the integration is established using the right protocols, a salesperson can access current billing period figures for a given client by going to that client’s profile in the sales database and generating a request. Simultaneously, a billing specialist could trigger an inquiry from the billing system to the sales database and then download knowledge regarding the newest contract rates available to a customer. In this case, BPI can ensure that customer orders are processed, executed, billed, and managed easily.
BPM Integration Vs. Business Process Integration[7]
Integration in the context of a BPM platform is a feature that allows the software to merge data across other systems. But it’s easy to see why BPM integration is often confused as a concept with business process integration (BPI). Both sound alike, but Business Process Integration is a distinct practice in itself that occurs when multiple business processes across multiple verticals work together to meet defined enterprise goals. For instance, when a e-commerce vendor receives a customer order for a smartphone listed on its website, it turns around to the phone manufacturer to check for availability or information on standard shipment time. In such scenarios, BPMs running across multiple channels integrate together for a symbiotic effect of delivering an end goal. Companies can use enterprise BPM system integration to achieve larger business process integration goals.
See Also
- Application Integration
- Enterprise Application Integration (EAI)
- Data Integration
- Enterprise Integration
- Enterprise Information Integration (EII)
- Customer Data Integration (CDI)
- Post Merger Integration (PMI)
References
- ↑ Defining Business Process Integration -Lansa
- ↑ What is Business Process Integration -Mulesoft
- ↑ The issue with Business Process Integration (BPI) S-Cube
- ↑ Business Process Integration Software Pega
- ↑ Types of Business Process Integration (BPI) Tallyfly
- ↑ Four Steps to a Successful Business Process Integration Solution Ingram Micro Advisor
- ↑ BPM Integration Versus Business Process Integration Kissflow
Further Reading
- Ground rules for managing business process integration projects IBM
- Creating Business Value Through Integration David Chappell
- Business Process Integration: How to Achieve Interoperability through Process Patterns Moufida Aouachria ; Abderrahmane Leshob ; Javier Gonzalez-Huerta ; Abdessamed Reda Ghomari ; Pierre Hadaya
- Process Integration Benefits and Challenges National Academies Press
- Business process integration as a solution to the implementation of supply chain management systems Takashi Kobayashia, MasatoTamakia, NorihisaKomodab
- Business Process Integration: Method and Analysis Evan D. Morrison, Alex Menzies, George Koliadis, Aditya K. Ghose
- BPI - Business Process based application Integration Kazuyuki Aoyama
