Component Business Model (CBM)
Component Business Model (CBM) is a technique developed by IBM to model and analyze an enterprise. It is a logical representation or map of business components or "building blocks" and can be depicted on a single page. It can be used to analyze the alignment of enterprise strategy with the organization's capabilities and investments, identify redundant or overlapping business capabilities, analyze sourcing options for the different components (buy or build), prioritize transformation options, and can be used to create a unified roadmap after mergers or acquisitions. The model is organized as business components along columns and "operational levels" along rows. The Business components are defined partly as large business areas with characteristic skills, IT capabilities, and processes. The three operational levels are "Direct", "Control" and "Execute" - they separate strategic decisions (Direct), management checks (Control), and business actions (Execute) on business competencies.[1]
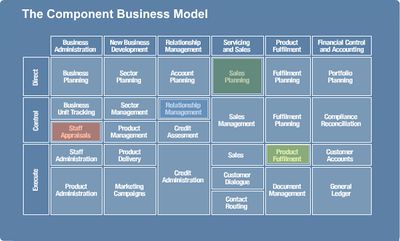
source: [3]
A Business Component is a logical view of part of an enterprise. It has discrete boundaries, defined by the business services that it offers and the business services it uses. It includes the resources, people, technology, and know-how necessary to deliver some value and is a ‘black box’ in the sense that the users don’t need to see the business activities that are inside. The Business Component can have attributes, such as cost, revenue, and importance to the business. Business services are goods or services that a business component offers to other business components and possibly to external parties.
CBM is not simply a way to imagine the future of the organization. It can also be used to put theory into action and drive the evolution toward a specialized enterprise, both internally and externally. This process involves three dimensions: one, developing a component view of the existing organization based on analysis of the business and the market environment; two, evolving toward specialization based on a reinvention plan within the context of changing industry dynamics; and three, advancing the organizational and operational infrastructure toward component-based enterprise optimization.
The key concepts of CBM are business components and accountability level:
- Business components are the essential and unique non-overlapping building blocks that make up the business and mission of an enterprise. They have the potential to operate independently, in the extreme as a separate unit, shared service, contractor-managed, or outsourced component.
- The accountability level characterizes the scope and intent of activity and decision-making at three levels:
- Directing is about strategy, overall direction, and policy.
- Controlling is about monitoring, managing exceptions, and tactical decision-making.
- Executing is about doing the work.[2]
See Also
- IT Strategy (Information Technology Strategy)
- Information Framework (IFW): Structured approach to managing and using information, supporting the execution and integration of various business model components.
- Business Model: Overview of different types of business models and their components.
- Business Strategy: How business models align with and support overall business objectives.
- Value Proposition: The value a company promises to deliver to customers through its business model.
- Business Architecture: The structure of a business, including its components, relationships, and processes.
- Enterprise Architecture: Framework for aligning IT strategy with business strategy, often including business models like CBM.
- Capabilities Mapping: Identifying and mapping the key capabilities needed to deliver the value proposition.
- Business Capability: The specific capabilities a business needs to execute its business model and strategy.
- Process Improvement: Techniques and methodologies for improving business processes.
- IT Governance: Framework ensuring IT supports and enables the business model and overall strategy.
- Digital Transformation (DX): The integration of digital technology into all areas of a business, fundamentally changing how it operates and delivers value.
- Innovation Management: Managing processes involved in the innovation of business models and practices.
- Strategic Planning: The process of defining strategy and making decisions on allocating resources to pursue this strategy.
- Change Management: Processes for managing organizational change effectively.
- Performance Management: Methods to monitor and manage the efficiency and effectiveness of the business model.
- Service Management: Managing the delivery of services in a way that maximizes value to customers and aligns with the business model.
- Agile Methodology: Approach to project management that is often used to iterate and improve business models rapidly.
- Risk Management: Identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks in strategic planning and execution.
- Customer Segments: Different groups of people or organizations a business aims to serve.
- Revenue Model: The strategy for generating income, which is a core component of the business model.
- Cost Structure: Breakdown of costs involved in operating the business model.
- Balanced Scorecard: Performance management tool that provides a view of an organization's overall performance.
- Lean Startup: Methodology for developing businesses and products, focusing on customer feedback and iterative design.
