IT Strategy Framework
What is an IT Strategy Framework?
An IT Strategy Framework defines the essential elements or components of IT Strategy, and their inter-relationship.
- A framework provides the logical or conceptual underpinnings that support an IT strategy
- An IT Strategy Framework is analogous to a mathematical equation or chemical formula in that it specifies the variables or elements and their relationships required to solve the "IT enabled or driven creation of business value" puzzle.
- It differs from equations and formulas in that it pertains to one solution - a particular way of solving the strategic puzzle - and is not a universally applicable or accepted answer to the strategy problem. There can be many different frameworks for IT strategy, each as applicable and effective as the other.
- It identifies "essential" elements or components i.e., those that are absolutely necessary and sufficient to define the concept or solution
An information technology strategy framework provides the structure and guidelines to develop a robust IT strategy that aligns technology with the organization's goals.
An IT Strategy Framework can define the strategic IT concept(s) in general or relate to a specific IT Strategy solution. Many different frameworks can be used to develop an IT strategy, and the best one for a particular organization will depend on its specific needs and goals.
What are the Essential Elements of an IT Strategy Framework?
A typical IT strategy framework includes the following components:
- Business objectives: Clarifying the business goals the IT strategy aims to support.
- Current state assessment: Analyzing the organization's technology infrastructure, processes, and capabilities.
- Future state vision: Defining a clear vision for the future state of technology within the organization.
- IT initiatives: Identifying specific technology projects and initiatives to support the vision and achieve the business goals.
- Prioritization: Determining the priority of the IT initiatives based on factors such as impact, feasibility, and cost.
- Implementation plan: Develop a plan for executing the IT initiatives, including timelines, budgets, and resource requirements.
- Governance: Establishing governance processes to ensure alignment between IT and business goals, manage risks, and monitor progress.
How is a Framework used in the Technology Strategic Planning Process?
A framework provides the conceptual foundation for the IT strategy process. It can make the process not only rapid and repeatable but also one that produces results.
- Define business goals: The first step in the IT Strategic Planning process is to define the organization's business goals. A framework can help clarify and prioritize these goals, providing a basis for developing the IT strategy.
- Assess current state: The next step is to assess the organization's current technology infrastructure, processes, and capabilities. A framework can be used to guide this assessment and provide a baseline for the future state vision.
- Develop future state vision: Based on the assessment of the current state and the organization's business goals, a framework can help develop a clear vision for the future state of technology and how it will support the business.
- Identify IT initiatives: The framework can identify specific technology projects and initiatives to support the future state vision and achieve the business goals.
- Prioritize Initiatives: The framework provides a structured approach for evaluating and prioritizing IT initiatives based on impact, feasibility, and cost.
- Develop implementation plan: The framework can be used to develop a detailed implementation plan for executing the IT initiatives, including timelines, budgets, and resource requirements.
- Establish governance: The framework can be used to establish governance processes to ensure alignment between IT and business goals, manage risks, and monitor progress.
By using an IT Strategy Framework in each step of the IT Strategic Planning process, organizations can ensure that their technology initiatives are aligned with their business goals, prioritize investments, and drive meaningful outcomes.
What is not included in an IT Strategy Framework?
An IT Strategy Framework does not include implementation considerations such as timing, steps, deliverables, roles or responsibilities.
- It does not provide any timing information on when to execute or create a component
- It does not provide the steps or sequence of execution
- It does not specify the deliverable(s) related to each component
- It does not specify who does what i.e. roles and responsibilities
Why do we need a framework for strategic planning of IT?
There are several reasons why frameworks can be useful in a variety of contexts, including IT strategy:
- They provide a structured approach: Frameworks provide a set of principles, concepts, or ideas that can be used to guide decision-making and problem-solving. This can help to ensure that important factors are considered and that a logical, structured approach is taken to addressing a particular issue or challenge in IT Strategy.
- They help to ensure consistency: Frameworks can help to ensure that decisions and actions are consistent with the goals and objectives of an organization. This can be particularly important in the context of IT strategy, where technology can significantly impact the overall direction and performance of the business.
- They facilitate communication and collaboration: Frameworks can help to provide a common language and understanding among stakeholders, which can facilitate communication and collaboration. This can be especially important in IT strategy, where different departments or business units may have different perspectives or priorities.
- They provide a reference point: Frameworks can serve as a reference point or benchmark against which progress can be measured. This can help to ensure that an organization stays on track and that its efforts are focused on the most important priorities.
- They can save time and resources: By providing a structured approach and a pre-defined set of guidelines, frameworks can save time and resources that would otherwise be spent on developing these elements from scratch. This can be especially important in IT strategy, where developing a comprehensive plan can be complex and resource-intensive.
- They can improve decision-making: By providing a structured approach and a set of guidelines for analyzing and evaluating different options and alternatives, frameworks can help to improve the quality of decision-making. This can be especially important in IT strategy, where the impact of different technology investments can be significant and long-lasting.
- They can help to identify and prioritize opportunities: Frameworks can help to identify and prioritize opportunities for improvement, innovation, or growth. This can be particularly important in IT strategy, where there may be many different options for using technology to support the business.
- They can provide a basis for learning and development: By providing a structured approach and a set of best practices, frameworks can serve as a basis for learning and development. This can be especially important in IT strategy, where technological change can be rapid, and organizations must keep up with new developments.
- They can help to ensure compliance: In some cases, frameworks may be required by law or regulations, or they may be used to ensure compliance with industry standards or best practices. In the context of IT strategy, this can be particularly important in industries that are subject to strict regulatory requirements or that have high security or privacy concerns.
- They can improve efficiency and effectiveness: By providing a structured approach and a set of best practices, frameworks can help to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of an organization's operations. This can be especially important in the context of IT strategy, where the use of technology can have a significant impact on the overall efficiency and effectiveness of the business.
- They can facilitate innovation: By providing a structured approach and a set of best practices, frameworks can help to facilitate innovation by providing a basis for experimentation and the testing of new ideas. This can be especially important in IT strategy, where technology can be a key driver of innovation and competitive advantage.
- They can provide a reference point for benchmarking: By providing a set of best practices or guidelines, frameworks can serve as a reference point for benchmarking an organization's performance against other organizations in the same industry or sector. This can be especially important in IT strategy, where it can be useful to compare an organization's use of technology with that of its competitors.
- They can help to ensure that resources are used effectively: By providing a structured approach and a set of best practices, frameworks can help to ensure that resources are used effectively and efficiently. This can be especially important in IT strategy, where technology can be resource-intensive, and it is important to maximize the return on investment.
- They can help to foster a culture of continuous improvement: By providing a structured approach and a set of best practices, frameworks can help to foster a culture of continuous improvement within an organization. This can be especially important in IT strategy, where technology is constantly evolving, and it is important to stay updated with new developments.
- They can help to build trust and confidence: By providing a structured approach and a set of best practices, frameworks can help to build trust and confidence among stakeholders. This can be especially important in the context of IT strategy, where the use of technology can be complex. It is important to ensure that stakeholders have confidence in the decisions.
It's worth noting that while frameworks can be useful in many situations, they are not a one-size-fits-all solution, and they may not be appropriate or necessary in all cases. It's important to consider the needs and goals of an organization carefully and to choose the most appropriate framework based on those needs. In some cases, it may be necessary to modify or adapt a framework to fit the specific needs of an organization better. Additionally, it's important to remember that frameworks are not a substitute for good judgment and critical thinking, and they should be used as a guide rather than as a rigid set of rules.
Creating an Effective IT Strategy Framework (Process steps)
Creating an IT strategy framework involves a systematic approach to aligning your organization's IT goals and objectives with its overall business strategy. Here's a step-by-step guide to help you create an IT strategy framework:
- Understand the business strategy: Begin by thoroughly understanding your organization's business strategy, objectives, and goals. Identify how technology can enable and support those objectives.
- Assess the current state: Evaluate your organization's IT infrastructure, systems, and processes. Identify strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats related to technology. Consider factors such as existing resources, budget, skills, and infrastructure.
- Define IT objectives: Based on the business strategy and assessment of the current state, establish clear and measurable IT objectives that align with the organization's goals. These objectives should be specific, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART).
- Identify IT initiatives: Determine the key initiatives and projects required to achieve the identified IT objectives. Consider infrastructure, applications, data management, cybersecurity, digital transformation, and innovation. Prioritize initiatives based on their strategic importance and potential impact.
- Allocate resources: Assess the resources (financial, human, and technical) required to implement the identified initiatives. Develop a resource allocation plan that outlines how resources will be allocated to each initiative. Consider budget, staffing, training, and partnerships with external vendors or consultants.
- Develop an implementation roadmap: Create a roadmap that outlines the sequence and timeline for implementing the IT initiatives. Consider dependencies between initiatives, resource availability, and potential risks. Define milestones and key performance indicators (KPIs) to track progress and measure success.
- Risk management: Identify potential risks and challenges associated with implementing the IT strategy. Develop strategies to mitigate and manage those risks. Consider risks related to security, data privacy, regulatory compliance, technology obsolescence, and change management.
- Communication and stakeholder engagement: Communicate the IT strategy framework to key stakeholders, including senior leadership, IT teams, and other relevant departments. Seek their feedback and involvement throughout the process. Create a communication plan to ensure stakeholders are informed about the progress and benefits of the IT strategy.
- Implementation and monitoring: Execute the IT strategy by implementing the initiatives according to the defined roadmap. Monitor progress regularly and track KPIs to ensure the strategy is on track. Make adjustments based on feedback, emerging technologies, and changing business needs.
- Evaluation and continuous improvement: Periodically evaluate the effectiveness of the IT strategy framework. Assess whether the objectives are being met and whether the initiatives deliver the expected outcomes. Use feedback and lessons learned to refine and improve the strategy over time.
Remember, an IT strategy framework should be flexible and adaptable to changing business and technological landscapes. Regularly review and update the framework to align with evolving organizational needs and emerging technologies.
Observe These Best Practices When Creating an IT Strategy Framework
When formulating an IT strategy framework, there are several best practices to remember. These practices will help ensure the effectiveness and success of your IT strategy. Here are some key best practices:
- Align IT with business goals: Your IT strategy should be closely aligned with the overall business goals and objectives of your organization. Ensure that your IT initiatives directly support and enable achieving these goals.
- Involve stakeholders: Engage key stakeholders throughout developing the IT strategy framework. This includes senior leadership, department heads, IT teams, and other relevant stakeholders. Gather their input, address their concerns, and ensure their buy-in. Collaboration and shared ownership of the strategy enhance its success.
- Conduct a thorough assessment: Before defining objectives and initiatives, conduct a comprehensive assessment of the current state of your IT infrastructure, systems, processes, and capabilities. Identify gaps, strengths, weaknesses, and opportunities. This assessment will inform your strategy and help you prioritize areas for improvement.
- Set clear and measurable objectives: Define clear, specific, and measurable objectives for your IT strategy. Make sure they are aligned with the overall business strategy. SMART objectives (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound) provide a framework for effective goal-setting.
- Prioritize initiatives: Determine the key initiatives and projects to drive your IT strategy forward. Prioritize these initiatives based on their strategic importance, potential impact, and available resources. Focus on initiatives that offer the highest value and align closely with business objectives.
- Secure executive sponsorship: Obtain executive sponsorship and support for your IT strategy. Senior leadership involvement is crucial for resource allocation, decision-making, and overcoming organizational barriers. Having a champion at the executive level helps ensure the strategy receives the necessary attention and resources.
- Develop a realistic implementation roadmap: Create a detailed implementation roadmap that outlines the sequence of initiatives, timelines, milestones, and resource allocation. Consider dependencies, potential risks, and the capacity of your organization to execute the plan. A well-structured roadmap helps ensure a smooth implementation process.
- Foster a culture of innovation: Encourage innovation and continuous improvement within your IT department and organization. Embrace emerging technologies, explore new opportunities, and encourage experimentation. This mindset enables you to adapt to changing business needs and leverage technology advancements.
- Emphasize change management: Recognize that implementing an IT strategy involves organizational change. Develop a change management plan that includes communication, training, and support for employees impacted by the strategy. Address resistance to change proactively and ensure stakeholders understand the benefits and rationale behind the strategy.
- Monitor and evaluate progress: Continuously monitor the progress of your IT strategy implementation. Establish key performance indicators (KPIs) and metrics to measure success. Regularly evaluate the strategy's effectiveness and adjust to address deviations or emerging challenges.
- Promote agility and adaptability: IT strategies should be flexible and adaptable to changing business and technology landscapes. Foster an agile mindset that allows for course corrections and adjustments as needed. Embrace emerging technologies and trends to stay ahead of the curve.
By following these best practices, you can create an IT strategy framework that effectively aligns technology with your organization's goals, enhances operational efficiency, and drives business growth.
Use These Tips and Tricks to Formulate an IT Strategy Framework
Developing an effective IT strategy framework requires careful planning and consideration. Here are some tips and tricks to help you in the process:
- Understand the business context: Gain a deep understanding of your organization's business context, industry trends, and competitive landscape. This knowledge will help you align your IT strategy with the specific needs and goals of your organization.
- Involve cross-functional teams: Include representatives from various departments and teams in the IT strategy development process. This cross-functional collaboration ensures a holistic approach and encourages a broader perspective on IT needs and opportunities.
- Conduct a SWOT analysis: Perform a comprehensive analysis of your organization's strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats (SWOT). This analysis will inform your IT strategy by identifying areas where technology can address weaknesses, capitalize on strengths, exploit opportunities, and mitigate threats.
- Leverage external expertise: Seek input from external consultants or industry experts who can provide insights and best practices relevant to your IT strategy. They can offer fresh perspectives, identify blind spots, and help validate your approach.
- Prioritize initiatives based on impact and feasibility: Assess the potential impact and feasibility of each initiative in your IT strategy. Prioritize initiatives with a high potential for positive impact and are feasible to implement within the available resources and constraints.
- Consider scalability and future-proofing: Design your IT strategy with scalability and future-proofing in mind. Anticipate future needs and emerging technologies to ensure your strategy can adapt and evolve over time. This approach minimizes the need for frequent major overhauls.
- Define clear roles and responsibilities: Clearly define the roles and responsibilities of key stakeholders involved in implementing the IT strategy. This clarity ensures accountability, avoids confusion, and facilitates effective collaboration.
- Communicate effectively: Develop a communication plan to inform stakeholders about the IT strategy, its goals, and progress. Regularly communicate updates, successes, and challenges to maintain engagement and support throughout the implementation process.
- Seek feedback and iterate: Seek stakeholder feedback during the development and implementation phases. Incorporate their input, address concerns, and iterate on your strategy as necessary. This iterative approach helps ensure the final strategy is well-aligned and has broad support.
- Monitor and measure progress: Establish metrics and key performance indicators (KPIs) to track the progress and impact of your IT strategy. Regularly monitor these metrics and measure them against your targets. This allows you to make data-driven decisions and identify areas that require adjustments.
- Foster a culture of innovation: Cultivate a culture of innovation within your organization. Encourage employees to explore new ideas, experiment with emerging technologies, and share their insights. Embrace a growth mindset that embraces continuous learning and improvement.
- Stay updated on industry trends: Continuously educate yourself about the latest industry trends, technological advancements, and best practices in IT strategy. This ongoing learning helps you stay ahead of the curve and make informed decisions.
Remember, an effective IT strategy framework is not a one-time activity. It requires regular evaluation, refinement, and adaptation to stay aligned with the changing needs of your organization and the evolving IT landscape.
Avoid These Common Mistakes and Pitfalls When Creating an IT Strategy Framework
When creating an IT strategy framework, it's important to be aware of common mistakes that can hinder its effectiveness. Here are some common mistakes to avoid:
- Lack of alignment with business goals: One of the most common mistakes is developing an IT strategy that is not closely aligned with the overall business goals and objectives. It's crucial to understand the organization's strategic direction and ensure that the IT strategy supports and enables those goals.
- Insufficient stakeholder involvement: Failing to involve key stakeholders throughout the process can lead to a lack of buy-in and support for the IT strategy. It's important to engage stakeholders from different departments and levels of the organization to gather diverse perspectives and ensure their needs and concerns are addressed.
- Neglecting a comprehensive assessment: Skipping or rushing through the assessment phase can result in an incomplete understanding of the current state of IT infrastructure, systems, and processes. A thorough assessment helps identify areas for improvement, potential risks, and opportunities that should inform the strategy.
- Lack of prioritization: Not prioritizing initiatives based on their strategic importance and potential impact can lead to resource allocation issues and delays. It's essential to assess and prioritize initiatives to focus on those that deliver the most value and align closely with the organization's objectives.
- Ignoring scalability and future-proofing: Failing to consider scalability and future needs can result in an IT strategy that quickly becomes outdated or requires major overhauls. It's important to anticipate future requirements and emerging technologies to ensure the strategy remains relevant and adaptable.
- Inadequate communication and change management: Poor communication and insufficient change management efforts can hinder the successful implementation of the IT strategy. It's important to develop a clear communication plan to keep stakeholders informed, address concerns, and actively manage the organizational change associated with the strategy.
- Lack of monitoring and evaluation: Neglecting to establish metrics, KPIs, and a system for monitoring and evaluating the progress of the IT strategy can make it challenging to assess its effectiveness. Regular monitoring and evaluation are essential for identifying deviations, making adjustments, and ensuring the strategy stays on track.
- Overlooking cybersecurity and risk management: Failing to prioritize cybersecurity and risk management can expose the organization to significant vulnerabilities. It's crucial to integrate robust security measures and risk management strategies into the IT strategy to protect sensitive data and mitigate potential threats.
- Insufficient investment in talent and skills: Underestimating the importance of investing in the development of IT talent and skills can hinder the successful implementation of the strategy. It's essential to assess the skills and competencies required and allocate resources for training, hiring, or partnering with external experts when necessary.
- Lack of flexibility and adaptability: Creating a rigid IT strategy that doesn't allow for adjustments in response to changing business needs and technological advancements can limit its effectiveness. It's important to foster a culture of agility and embrace emerging technologies to stay ahead of the curve.
By avoiding these common mistakes and addressing potential pitfalls, you can enhance the chances of creating an effective IT strategy framework that aligns with your organization's goals and drives meaningful business outcomes.
IT Strategy Framework Examples
This diagram depicts a process to create an IT Strategy. It is not, however, an IT strategy framework because it does not define the essential - necessary and sufficient - elements of an IT Strategy, nor their inter-relationship.
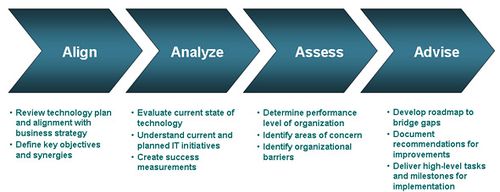
Source:Synch-Solutions
This diagram depicts an IT Strategy Framework as it lists the key parts of an IT strategic plan. However, it could be enhanced to provide the relationship between these elements.
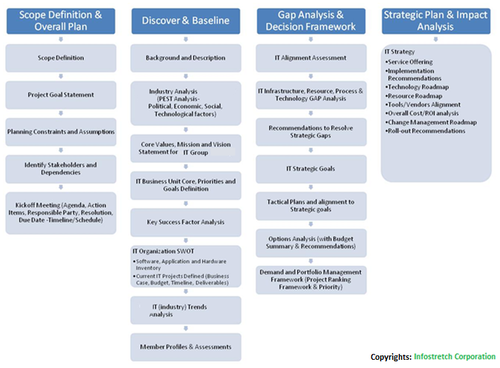
Source: InfoStretch Corporation
Key IT Strategy Frameworks
Difference Between Framework and Methodology
IT Strategy Methodology adds implementation considerations such as timing, steps, deliverables, roles and responsibilities to an IT Strategy Framework.
Therefore, an IT Strategy Methodology makes an IT Strategy Framework usable. However, this comes at a cost - a methodology's rigor adds rigidity to a solution. Now, work must be done to adapt it to different situations. Often, this creates issues because of resistance from methodology zealots who have long lost touch with the underlying framework.
Difference Between Framework and Template
A framework is a structured approach or set of guidelines that an organization can use to guide the creation of a strategy for information technology. A template, on the other hand, is a pre-formatted document or tool that can be used as a starting point for creating a new document or project.
A framework provides a set of principles, concepts, or ideas that can be used as a basis for analyzing and evaluating an IT strategy while a template typically includes pre-defined formatting, layout, and content that can be customized to fit the specific needs of a particular organization.
One key difference between a framework and a template is that a framework is more flexible and adaptable, while a template is more specific and prescriptive. A framework provides a set of guidelines that can be applied in a variety of different situations, while a template is designed for a specific purpose and may be less adaptable to other uses.
For example, an IT strategy framework might provide a set of principles and best practices for developing and implementing an IT strategy, while an IT strategy template might provide a pre-formatted document that includes specific sections and formatting for creating an IT strategic plan. In this case, the framework would provide the general guidelines and principles that should be followed, while the template would provide a specific tool for creating a document based on those guidelines.
A template transforms a framework into a deliverable. It fills in the pieces required to take a concept to a practical solution. A framework is logical whereas a template is physical.
A framework can be used to develop a template by providing a structured approach or set of guidelines that can be used as the basis for creating the template. The framework can be used to identify the key elements or components that should be included in the template, and to provide guidance on how those elements should be structured or formatted.
For example, suppose an organization is developing a template for an IT strategy plan. In that case, it might use an IT strategy framework to identify the key elements that should be included in the plan, such as a description of the current state of the organization's IT systems, a vision for the future direction of the IT function, and a roadmap for achieving that vision. The framework might also provide guidance on how to structure the document, such as by including sections on strategic objectives, key initiatives, and performance metrics.
To use a framework to develop a template, the following steps might be followed:
- Identify the purpose and goals of the template: Determine what the template will be used for and what its overall goals and objectives are.
- Select a suitable framework: Choose a framework that is relevant to the purpose and goals of the template and that provides the appropriate level of guidance and structure.
- Identify the key elements and components: Use the framework to identify the key elements and components that should be included in the template.
- Define the structure and formatting: Use the framework to define the overall structure and formatting of the template, including the layout, headings, and content for each section.
- Create the template: Use the framework as a guide to create the template, following the guidelines and principles set out in the framework to ensure that the template is structured and formatted in a way that meets the needs and goals of the organization.
- Test and refine the template: Once the template has been created, it is important to test it to ensure that it is effective and meets the needs of the organization. This may involve using the template to create a sample document or project and reviewing it to identify any areas that need improvement or refinement.
- Update and maintain the template: As the needs of the organization change over time, it may be necessary to update and maintain the template to ensure that it continues to be relevant and effective. This may involve revising the content or formatting of the template, or adding new elements or components as needed.
Using a framework to develop a template can be a useful way to ensure that the template is structured and formatted in a way that is consistent with the goals and objectives of the organization. It can also help to ensure that the template is flexible and adaptable, and can be used in a variety of different situations. By following a structured approach and using a framework as a guide, organizations can create templates that are effective and meet their specific needs.
An IT strategy framework is particularly important in today's rapidly changing technological environment, where the use of technology can have a significant impact on the overall direction and performance of a business. By providing a structured approach and a set of best practices, an IT strategy framework can help organizations navigate the complexities of technology and to make informed decisions about the use of IT to support their business goals.
Overall, an IT strategy framework is an essential tool for any organization that is looking to effectively use technology to support and achieve its business objectives.
