Business Valuation
Business Valuation is a process and a set of procedures used to estimate the economic value of an owner's interest in a business. Valuation is used by financial market participants to determine the price they are willing to pay or receive to effect a sale of a business. In addition to estimating the selling price of a business, the same valuation tools are often used by business appraisers to resolve disputes related to estate and gift taxation, divorce litigation, allocate business purchase price among business assets, establish a formula for estimating the value of partners' ownership interest for buy-sell agreements, and many other business and legal purposes such as in shareholders deadlock, divorce litigation and estate contest. In some cases, the court would appoint a forensic accountant as the joint expert doing the business valuation. In these cases, attorneys should always be prepared to have their expert’s report withstand the scrutiny of cross-examination and criticism.[1]
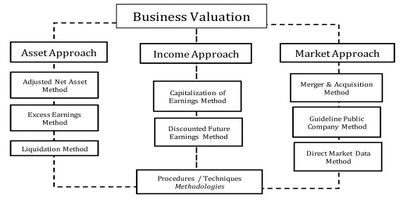
Business Valuation Approaches[2]
There are conceptually three broad approaches in business valuation
- Asset-Based Approaches (Asset Approach): Essentially, an asset-based business valuation will total up all the investments in the company. Asset-based business valuations can be done in one of two ways:
- A going concern asset-based approach takes a look at the company's balance sheet, lists the business's total assets, and subtracts its total liabilities. This is also called book value.
- A liquidation asset-based approach determines the liquidation value, or the net cash that would be received if all assets were sold and liabilities paid off.
- Earning Value Approaches (Income Approach): An earning value approach is based on the idea that a business's value lies in its ability to produce wealth in the future.
- Capitalizing Past Earning determines an expected level of cash flow for the company using a company's record of past earnings, normalizes them for unusual revenue or expenses, and multiplies the expected normalized cash flows by a capitalization factor. The capitalization factor is a reflection of what rate of return a reasonable purchaser would expect on the investment, as well as a measure of the risk that the expected earnings will not be achieved.
- Discounted Future Earnings is another earning value approach to business valuation where instead of an average of past earnings, an average of the trend of predicted future earnings is used and divided by the capitalization factor.
- Market Value Approach (Market Approach): Market value approaches to business valuation attempt to establish the value of your business by comparing your company to similar ones that have recently sold. The idea is similar to using real estate comps, or comparables, to value a house. This method only works well if there are a sufficient number of similar businesses to compare.
source: American Business Appraisers
One of these methods is earnings driven; one is market driven; and the other utilizes the assets of the Company to determine value. The earnings driven method is typically more appropriate, because it accords primary consideration to the historical/future earnings potential of the Company. In concept, a market driven method follows the goal in the appraisal process, which is to estimate what could reasonably be expected to occur in the market, as it is based on what has occurred in the market. Its limitations are the extent to which data is available on transactions and the imprecision associated with determining the extent to which the companies sold were sufficiently similar to be judged “equally desirable substitutes”. Asset-based method provides an alternative method, but one which is less appropriate for primarily two reasons: (i) the business valuation community is in agreement that earnings should be pre-eminent; and (ii) adjustments made to the balance sheet are less precise, particularly regarding valuing the fixed assets.
- ↑ Definition - What is Business Valuation? Wikipedia
- ↑ Business Valuation Approaches the balance
