Component Business Model (CBM)
Component Business Model (CBM) is a technique developed by IBM to model and analyze an enterprise. It is a logical representation or map of business components or "building blocks" and can be depicted on a single page. It can be used to analyze the alignment of enterprise strategy with the organization's capabilities and investments, identify redundant or overlapping business capabilities, analyze sourcing options for the different components (buy or build), prioritizing transformation options and can be used to create a unified roadmap after mergers or acquisitions. The model is organized as business components along columns and "operational levels" along rows. The Business components are defined partly as large business areas with characteristic skills, IT capabilities and process. The three operational levels are "Direct", "Control" and "Execute" - they separate strategic decisions (Direct), management checks (Control), and business actions (Execute) on business competencies.[1]
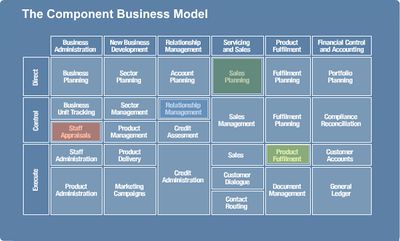
source: [1]
CBM is not simply a way to imagine the future of the organization. It can also be used to put theory into action and drive the evolution toward a specialized enterprise, both internally and externally. This process involves three dimensions: one, developing a component view of the existing organization based on analysis of the business and the market environment; two, evolving toward specialization based on a reinvention plan within the context of changing industry dynamics; and three, advancing the organizational and operational infrastructure toward component-based enterprise optimization.[2]
