Difference between revisions of "Customer Data Management (CDM)"
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
| − | [[File:Components_of_CDM.png| | + | [[File:Components_of_CDM.png|500px|Components of Customer Data Management]]<br /> |
source: Techtarget | source: Techtarget | ||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
*Allow stakeholders to identify and contact a target audience segment | *Allow stakeholders to identify and contact a target audience segment | ||
*Allow stakeholders to identify and contact specific marketing qualified leads (MQLs) and sales qualified leads (SQLs). | *Allow stakeholders to identify and contact specific marketing qualified leads (MQLs) and sales qualified leads (SQLs). | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | == See Also == | ||
| + | [[Customer]]<br /> | ||
| + | [[Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC)]]<br /> | ||
| + | [[Customer Centricity]]<br /> | ||
| + | [[Customer Demographics]]<br /> | ||
| + | [[Customer Due Diligence (CDD)]]<br /> | ||
| + | [[Customer Dynamics]]<br /> | ||
| + | [[Customer Effort Score (CES)]]<br /> | ||
| + | [[Customer Engagement]]<br /> | ||
| + | [[Customer Engagement Hub (CEH)]]<br /> | ||
| + | [[Customer Experience Management (CEM)]]<br /> | ||
| + | [[Customer Lifecycle]]<br /> | ||
| + | [[Customer Lifetime Value]]<br /> | ||
| + | [[Customer Loyalty]]<br /> | ||
| + | [[Customer Needs]]<br /> | ||
| + | [[Customer Retention]]<br /> | ||
| + | [[Customer Service]]<br /> | ||
| + | [[Customer Service Management]]<br /> | ||
| + | [[Customer Relationship Management (CRM)]]<ref> | ||
| + | [[Customer Data Integration (CDI)]]<br /> | ||
| + | [[Enterprise Data Integration (EDI)]]<ref> | ||
| + | [[Data Management]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | == References == | ||
| + | <references/> | ||
Revision as of 19:00, 11 October 2019
Customer Data Management (CDM) is a solution mechanism in which an organization's customer data is collected, managed and analyzed. CDM is geared toward resolving customer requirements and issues while enhancing customer retention and satisfaction, allowing an organization to convert customer data into Customer Intelligence (CI). With CDM, one or more software applications are integrated to facilitate access to reliable and efficient customer data. Attracting and retaining customers requires a clear understanding of customer requirements. CDM streamlines customer relationship management (CRM), marketing and customer feedback management (CFM).[1]
Customer data management is defined as the people, processes, technologies, and systems that collect, analyze, and organize customer data.
source: MarTech Advisor
Background of Customer Data Management (CDM)[2]
Customer data management, as a term, was coined in the 1990s, pre-dating the alternative term enterprise feedback management (EFM). CDM was introduced as a software solution that would replace earlier disc-based or paper-based surveys and spreadsheet data. Initially, CDM solutions were marketed to businesses as software, specific to one company, and often to one department within that company. This was superseded by application service providers (ASPs) where software was hosted for end user organizations, thus avoiding the necessity for IT professionals to deploy and support software. However, ASPs with their single-tenancy architecture were, in turn, superseded by software as a service (SaaS), engineered for multi-tenancy. By 2007 SaaS applications, giving businesses on-demand access to their customer information, were rapidly gaining popularity compared with ASPs. Cloud computing now includes SaaS and many prominent CDM providers offer cloud-based applications to their clients.
In recent years, there has been a push away from the term EFM, with many of those working in this area advocating the slightly updated use of CDM. The return to the term CDM is largely based on the greater need for clarity around the solutions offered by companies, and on the desire to retire terminology veering on techno-jargon that customers may have a hard time understanding.
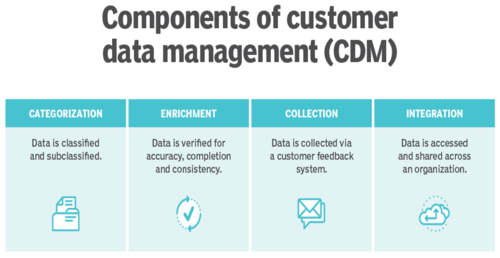
Components of Customer Data Management (CDM)[3]
CDM must be tightly integrated across the departments of an organization, including IT, sales and HR. CDM components include:
- Categorization: Customer data is classified and subclassified.
- Correction: Collected data is verified for accuracy and consistency. When necessary, contact details are updated, and duplicate records are removed.
- Enrichment: Incomplete data is collected and completed.
- Collection: Customer data and insight activity is collected via a customer feedback system or sources, like sales, customer support, surveys, reports, newsletters and other customer interactions.
Customer data is organized and shared throughout an organization.
Organizations can implement CDM with in-house software tools or cloud computing services that collect, analyze and organize customer information in a single, consistent platform. Once in place, the data can be accessed in real time by all relevant departments across the entire organization, including sales, marketing and customer support. CDM software products can be used in a variety of ways, such as:
- Allow stakeholders to initiate an instant response to customer feedback or issues.
- Allow stakeholders to identify and contact a target audience segment
- Allow stakeholders to identify and contact specific marketing qualified leads (MQLs) and sales qualified leads (SQLs).
See Also
Customer
Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC)
Customer Centricity
Customer Demographics
Customer Due Diligence (CDD)
Customer Dynamics
Customer Effort Score (CES)
Customer Engagement
Customer Engagement Hub (CEH)
Customer Experience Management (CEM)
Customer Lifecycle
Customer Lifetime Value
Customer Loyalty
Customer Needs
Customer Retention
Customer Service
Customer Service Management
Customer Relationship Management (CRM)<ref>
Customer Data Integration (CDI)
Enterprise Data Integration (EDI)<ref>
Data Management
References
- ↑ Defining Customer Data Management (CDM) Techopedia
- ↑ Background of Customer Data Management (CDM) Wikipedia
- ↑ Components of Customer Data Management (CDM) Techtarget