DMAIC Framework
The Major Steps in DMAIC[1]
Almost all implementations of Six Sigma employ DMAIC for project management and completion of process improvement projects. However, DMAIC is not necessarily formally tied to Six Sigma, and can be used regardless of an organization’s use of Six Sigma. It is a general and very useful approach to management of change and improvement. DMAIC is a generalization of Walter Shewhart’s Plan-Do-Check-Act cycle, which provides a roadmap to help people understand how to integrate the various tools into an overall approach to quality improvement.
The DMAIC steps are illustrated graphically in the Figure below . Notice that there are “tollgates” between each of the major steps in DMAIC. At a tollgate, a project team presents its work to managers and “owners” of the process. In a Six Sigma organization, the tollgate participants also would include the project Champion, MBBs, and other BBs not working directly on the project. Tollgates are where the project is reviewed to ensure that it is on track. They provide a continuing opportunity to evaluate whether the team can successfully complete the project on schedule. Tollgates also present an opportunity to provide guidance regarding the use of specific technical tools and other information about the problem. Organization problems and other barriers to success, as well as strategies for dealing with them, are often identified during tollgate reviews. Tollgates are critical to the overall problem-solving process. It is important that these reviews be conducted very soon after the team completes each step.
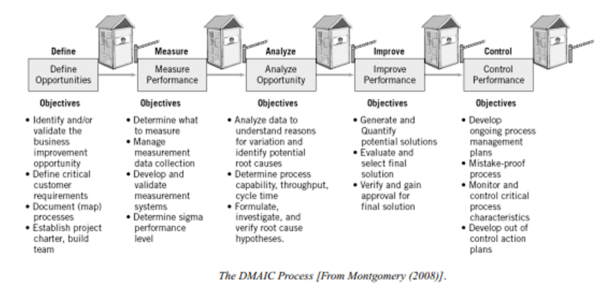
source: Douglas C. Montgomery and William H. Woodall
The DMAIC structure encourages creative thinking about the problem and its solution within the definition of the originalproduct, process, or service. When the process is operating so poorly that it is necessary to abandon the original process and start over, or if it is determined that a new product or service is required, then the improved step of DMAIC actually becomes a process design or re-design step. In a Six Sigma organization, that means that a design for Six Sigma (DFSS) effort is required.
- ↑ The Major Steps in DMAICDouglas C. Montgomery and William H. Woodall
