Difference between revisions of "Efficient Consumer Response (ECR)"
m (The LinkTitles extension automatically added links to existing pages (https://github.com/bovender/LinkTitles).) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | '''Efficient Consumer Response (ECR)''' is a system for replenishing merchandise based on actual consumer demand. Prior methods of inventory replenishment were order driven, relying on retailers and wholesalers to predict demand. ECR is demand driven, initiating the manufacture and shipment of goods based on consumer purchase activity. ECR reduces the cycle time from purchase to replenishment, reduces the cost of warehousing excess inventory, and assists retailers, wholesalers, and manufacturers in determining the optimum product mix. ECR predicts the impact of a product promotion on retail demand and production requirements. ECR is dependent upon the efficient and timely sharing of data along the [Supply-Chain-Management|supply chain] beginning with sales information collected at a point-of-sale terminal. Given thin margins on average transactions and significant expenditures on warehouse space, some food and drug retailers resist manufacturers’ ECR initiatives.<ref> Definition of Efficient Consumer Response (ECR) [https://www.allbusiness.com/barrons_dictionary/dictionary-ecr-efficient-consumer-response-4966358-1.html Allbusiness]</ref> | + | '''Efficient Consumer Response (ECR)''' is a [[system]] for replenishing merchandise based on actual consumer [[demand]]. Prior methods of [[inventory]] replenishment were order driven, relying on retailers and wholesalers to predict demand. ECR is demand driven, initiating the manufacture and shipment of goods based on consumer purchase activity. ECR reduces the cycle time from purchase to replenishment, reduces the cost of warehousing excess inventory, and assists retailers, wholesalers, and manufacturers in determining the optimum [[product]] mix. ECR predicts the [[impact]] of a product [[promotion]] on retail demand and production requirements. ECR is dependent upon the efficient and timely sharing of [[data]] along the [[[Supply]]-Chain-[[Management]]|supply chain] beginning with sales information collected at a point-of-sale terminal. Given thin margins on average transactions and significant expenditures on warehouse space, some food and drug retailers resist manufacturers’ ECR initiatives.<ref> Definition of Efficient Consumer Response (ECR) [https://www.allbusiness.com/barrons_dictionary/dictionary-ecr-efficient-consumer-response-4966358-1.html Allbusiness]</ref> |
| − | "ECR" is a strategic concept compiled by a consulting firm "Kurt Simon Associates " at the request of organizations concerning the U.S. processed food distribution industry, aiming to recover the competitive strength for surviving the turbulent time of the industry when discounters emerged in the U.S. For "ECR", reengineering such as eliminating or adding business operations is performed by checking all business operations of a supply chain of companies by a criterion of whether they contribute to providing higher values to consumers. This aims to provide better convenience, better products, better quality, better selection of goods and build a "Win - Win" relationship among companies concerned (i.e. every company of a supply chain wins and gains profits). The first target of ECR is to [[Business_Process_Reengineering_(BPR)|reengineer business processes]]. To realize the reengineering, information technology such as [[Electronic_Data_Interchange_(EDI)|EDI (Electronic Data Interchange)]] that is used for accurate and timely exchange of information between companies is necessary. Characteristics of ECR is that reengineering is performed considering final results given to consumers from unified business processes and that can be realized by information technology. It is said that whether a company carried out ECR or not obviously decided the fate of the company, either growth and prosperity or change or out of business.<ref>Efficient Consumer Response (ECR) - Concept [http://www.lean-manufacturing-japan.com/scm-terminology/ecr-efficient-consumer-response.html Lean Manufacturing Japan]</ref> | + | "ECR" is a strategic concept compiled by a consulting firm "Kurt Simon Associates " at the request of organizations concerning the U.S. processed food [[distribution]] [[industry]], aiming to recover the competitive strength for surviving the turbulent time of the industry when discounters emerged in the U.S. For "ECR", reengineering such as eliminating or adding [[business]] operations is performed by checking all business operations of a supply chain of companies by a criterion of whether they contribute to providing higher values to consumers. This aims to provide better convenience, better products, better [[quality]], better [[selection]] of goods and build a "Win - Win" relationship among companies concerned (i.e. every company of a supply chain wins and gains profits). The first [[target]] of ECR is to [[Business_Process_Reengineering_(BPR)|reengineer business processes]]. To realize the reengineering, information technology such as [[Electronic_Data_Interchange_(EDI)|EDI (Electronic Data Interchange)]] that is used for accurate and timely exchange of information between companies is necessary. Characteristics of ECR is that reengineering is performed considering final results given to consumers from unified business processes and that can be realized by information technology. It is said that whether a company carried out ECR or not obviously decided the fate of the company, either growth and prosperity or change or out of business.<ref>Efficient Consumer Response (ECR) - Concept [http://www.lean-manufacturing-japan.com/scm-terminology/ecr-efficient-consumer-response.html Lean Manufacturing Japan]</ref> |
| − | There are four focus areas of ECR. These areas are broken down further into core and advanced improvement concepts. Individually these concepts are commonly known and well documented methods to improve effectiveness and efficiency. However, when applied under ECR, they have two distinct differences: | + | There are four focus areas of ECR. These areas are broken down further into core and advanced [[improvement]] concepts. Individually these concepts are commonly known and well documented methods to improve effectiveness and [[efficiency]]. However, when applied under ECR, they have two distinct differences: |
*They are intended to be addressed as an integrated set, not individually; | *They are intended to be addressed as an integrated set, not individually; | ||
*They are assessed in terms of their impact across the entire supply chain, not just the business of individual trading partners.<ref>ECR Focus Areas [http://www.ecr-baltic.org/en/about-ecr/ecr-efficient-consumer-response/ ecr-baltic.org]</ref> | *They are assessed in terms of their impact across the entire supply chain, not just the business of individual trading partners.<ref>ECR Focus Areas [http://www.ecr-baltic.org/en/about-ecr/ecr-efficient-consumer-response/ ecr-baltic.org]</ref> | ||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
'''ECR Benefits'''<ref>Scope of ECR Benefits [http://www.just-style.com/analysis/part-1_id92925.aspx Just-Style]</ref><br /> | '''ECR Benefits'''<ref>Scope of ECR Benefits [http://www.just-style.com/analysis/part-1_id92925.aspx Just-Style]</ref><br /> | ||
| − | The anticipated benefits are broad. Grouped according to thefive dimensions of value chain performance, they include: | + | The anticipated benefits are broad. Grouped according to thefive dimensions of [[value]] chain performance, they include: |
*Cost | *Cost | ||
**ECR has the potential to reduce non-value-added activities and also to lower inventory. The financial benefits amount to around 5% of retail sales | **ECR has the potential to reduce non-value-added activities and also to lower inventory. The financial benefits amount to around 5% of retail sales | ||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
**ECR promotes better transmission of data and the synchronisation of activities within the value chain | **ECR promotes better transmission of data and the synchronisation of activities within the value chain | ||
*Quality | *Quality | ||
| − | **ECR enables consumers' expectations to be better met, through higher process and delivery reliability and the avoidance of the degradation of perishable goods | + | **ECR enables consumers' expectations to be better met, through higher [[process]] and delivery reliability and the avoidance of the degradation of perishable goods |
| − | *Customer service | + | *[[Customer]] [[service]] |
| − | **ECR leads to improved customer service in areas as diverse as the avoidance of stock-outs, the ability to be responsive to particular customer requests and the provision of stores that allow consumers to make choices more easily (e.g. by better designed store layouts and displays) | + | **ECR leads to improved customer service in areas as diverse as the avoidance of [[stock]]-outs, the ability to be responsive to particular customer requests and the provision of stores that allow consumers to make choices more easily (e.g. by better designed store layouts and displays) |
*Adaptability | *Adaptability | ||
**ECR explicitly targets new product introduction as a process to be improved | **ECR explicitly targets new product introduction as a process to be improved | ||
| Line 38: | Line 38: | ||
===External References=== | ===External References=== | ||
*The Case for ECR - A review and outlook of continuous ECR adoption in Western Europe [https://www.alexandria.unisg.ch/68389/1/TheCaseForECR.pdf ECR Europe, Brussles] | *The Case for ECR - A review and outlook of continuous ECR adoption in Western Europe [https://www.alexandria.unisg.ch/68389/1/TheCaseForECR.pdf ECR Europe, Brussles] | ||
| − | *Efficient Consumer Response (ECR): Adding Customer Value to the Supply Chain using Collaboration [http://cerasis.com/2014/05/20/efficient-consumer-response/ Chuck Intrieri] | + | *Efficient Consumer Response (ECR): Adding [[Customer Value]] to the [[Supply Chain]] using [[Collaboration]] [http://cerasis.com/2014/05/20/efficient-consumer-response/ Chuck Intrieri] |
*The Mutuality of ECR Benefits, Costs and Risks in Supply Chain Reform [https://www.researchgate.net/publication/254498266_The_Mutuality_of_ECR_Benefits_Costs_and_Risks_in_Supply_Chain_Reform Sherah Kurnia, Robert B. Johnston] | *The Mutuality of ECR Benefits, Costs and Risks in Supply Chain Reform [https://www.researchgate.net/publication/254498266_The_Mutuality_of_ECR_Benefits_Costs_and_Risks_in_Supply_Chain_Reform Sherah Kurnia, Robert B. Johnston] | ||
Revision as of 15:35, 6 February 2021
Efficient Consumer Response (ECR) is a system for replenishing merchandise based on actual consumer demand. Prior methods of inventory replenishment were order driven, relying on retailers and wholesalers to predict demand. ECR is demand driven, initiating the manufacture and shipment of goods based on consumer purchase activity. ECR reduces the cycle time from purchase to replenishment, reduces the cost of warehousing excess inventory, and assists retailers, wholesalers, and manufacturers in determining the optimum product mix. ECR predicts the impact of a product promotion on retail demand and production requirements. ECR is dependent upon the efficient and timely sharing of data along the [[[Supply]]-Chain-Management|supply chain] beginning with sales information collected at a point-of-sale terminal. Given thin margins on average transactions and significant expenditures on warehouse space, some food and drug retailers resist manufacturers’ ECR initiatives.[1]
"ECR" is a strategic concept compiled by a consulting firm "Kurt Simon Associates " at the request of organizations concerning the U.S. processed food distribution industry, aiming to recover the competitive strength for surviving the turbulent time of the industry when discounters emerged in the U.S. For "ECR", reengineering such as eliminating or adding business operations is performed by checking all business operations of a supply chain of companies by a criterion of whether they contribute to providing higher values to consumers. This aims to provide better convenience, better products, better quality, better selection of goods and build a "Win - Win" relationship among companies concerned (i.e. every company of a supply chain wins and gains profits). The first target of ECR is to reengineer business processes. To realize the reengineering, information technology such as EDI (Electronic Data Interchange) that is used for accurate and timely exchange of information between companies is necessary. Characteristics of ECR is that reengineering is performed considering final results given to consumers from unified business processes and that can be realized by information technology. It is said that whether a company carried out ECR or not obviously decided the fate of the company, either growth and prosperity or change or out of business.[2]
There are four focus areas of ECR. These areas are broken down further into core and advanced improvement concepts. Individually these concepts are commonly known and well documented methods to improve effectiveness and efficiency. However, when applied under ECR, they have two distinct differences:
- They are intended to be addressed as an integrated set, not individually;
- They are assessed in terms of their impact across the entire supply chain, not just the business of individual trading partners.[3]
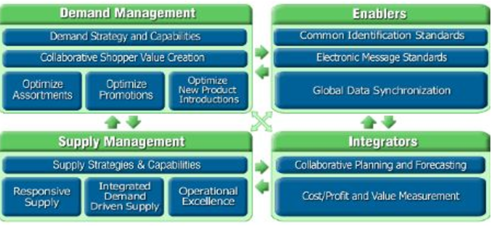
source: ecr-baltic.org
ECR Benefits[4]
The anticipated benefits are broad. Grouped according to thefive dimensions of value chain performance, they include:
- Cost
- ECR has the potential to reduce non-value-added activities and also to lower inventory. The financial benefits amount to around 5% of retail sales
- Timeliness
- ECR promotes better transmission of data and the synchronisation of activities within the value chain
- Quality
- ECR enables consumers' expectations to be better met, through higher process and delivery reliability and the avoidance of the degradation of perishable goods
- Customer service
- ECR leads to improved customer service in areas as diverse as the avoidance of stock-outs, the ability to be responsive to particular customer requests and the provision of stores that allow consumers to make choices more easily (e.g. by better designed store layouts and displays)
- Adaptability
- ECR explicitly targets new product introduction as a process to be improved
ECR Challenges[5]
Implementing ECR means dramatic change in current business practices. ECR challenges many existing approaches, which can often lead to inefficiency. Trading partners are asked to work together in order to increase value to the consumer. The intensifying competition amongst trading partners often presents an apparent barrier to achieving this. However, just the opposite is true – ECR allows companies to seek a competitive advantage by demonstrating their superior ability in working with trading partners to add value for the consumer.
References
- ↑ Definition of Efficient Consumer Response (ECR) Allbusiness
- ↑ Efficient Consumer Response (ECR) - Concept Lean Manufacturing Japan
- ↑ ECR Focus Areas ecr-baltic.org
- ↑ Scope of ECR Benefits Just-Style
- ↑ Challenges and Key Benefits of ECR ECR Community
External References
- The Case for ECR - A review and outlook of continuous ECR adoption in Western Europe ECR Europe, Brussles
- Efficient Consumer Response (ECR): Adding Customer Value to the Supply Chain using Collaboration Chuck Intrieri
- The Mutuality of ECR Benefits, Costs and Risks in Supply Chain Reform Sherah Kurnia, Robert B. Johnston
