Barcode
A barcode is an image that consists of a series of parallel black and white bars that can be read by a barcode scanner. Barcodes are applied to products to quickly identify them. Among their many uses, barcodes are typically used in retail stores as a part of the purchasing process, in warehouses to track and manage inventory and on invoices to help with accounting.[1]
The technical definition for a barcode is a machine-readable form of information on a scannable, visual surface. They are also often known as UPC codes. The barcode is read by using a special scanner that reads the information directly off of it. The information is then transmitted into a database where it can be logged and tracked. Merchandisers and other companies must pay an annual fee to an organization called The UCC, or Uniform Code Council, who then generates special barcodes specific to that particular company. Each number on a barcode has a special meaning, and often these numbers are added, multiplied, and divided in some formula that gives them each their own special identity. Barcodes are very useful for maintaining accurate information about inventory, pricing, and other important business-related data.[2]
Although barcode technology was originally patented in 1952, it wasn’t until 1974 that the first product—a package of Wrigley’s gum—was scanned at a Marsh® supermarket in Ohio. Today, barcodes come in dozens of different formats, from a row of simple lines called a 1D (one-dimensional) barcode to dots and squares that form a 2D (two-dimensional) code; QR (Quick Response) and Data Matrix codes are among the most popular 2D codes. The more advanced 2D code allows users to store and retrieve significantly more data than they could with a 1D code. This is because 1D codes only contain data in the horizontal direction whereas 2D codes contain information both vertically and horizontally.[3]
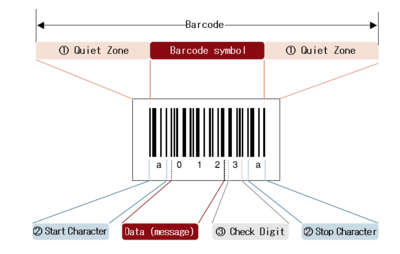
Barcode Components[4]
- Quiet Zone (margin): Quiet Zone is a blank margin located at either end of a barcode. The minimal margin between barcodes (distance from the outermost bar of one barcode to the outermost bar of another barcode) is 2.5 mm. If the width of a Quiet Zone is insufficient, barcodes are hard for a scanner to read.
- Start Character/Stop Character: The Start Character and the Stop Character are characters representing the start and the end of the data, respectively. The characters differ depending on the barcode type.
- Check Digit (Symbol check character): The Check Digit is a digit for checking whether the encoded barcode data are correct.
History of Barcodes[5]
In 1948 Bernard Silver, a graduate student at Drexel Institute of Technology in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, US overheard the president of the local food chain, Food Fair, asking one of the deans to research a system to automatically read product information during checkout. Silver told his friend Norman Joseph Woodland about the request, and they started working on a variety of systems. Their first working system used ultraviolet ink, but the ink faded too easily and was expensive.
Convinced that the system was workable with further development, Woodland left Drexel, moved into his father's apartment in Florida, and continued working on the system. His next inspiration came from Morse code, and he formed his first barcode from sand on the beach. "I just extended the dots and dashes downwards and made narrow lines and wide lines out of them." To read them, he adapted technology from optical soundtracks in movies, using a 500-watt incandescent light bulb shining through the paper onto an RCA935 photomultiplier tube (from a movie projector) on the far side. He later decided that the system would work better if it were printed as a circle instead of a line, allowing it to be scanned in any direction.
On 20 October 1949, Woodland and Silver filed a patent application for "Classifying Apparatus and Method", in which they described both the linear and bull's eye printing patterns, as well as the mechanical and electronic systems needed to read the code. The patent was issued on 7 October 1952 as US Patent 2,612,994. In 1951, Woodland moved to IBM and continually tried to interest IBM in developing the system. The company eventually commissioned a report on the idea, which concluded that it was both feasible and interesting, but that processing the resulting information would require equipment that was some time off in the future.
IBM offered to buy the patent, but the offer was not accepted. Philco purchased the patent in 1962 and then sold it to RCA sometime later.
Collins at Sylvania During his time as an undergraduate, David Jarrett Collins worked at the Pennsylvania Railroad and became aware of the need to automatically identify railroad cars. Immediately after receiving his master's degree from MIT in 1959, he started work at GTE Sylvania and began addressing the problem. He developed a system called KarTrak using blue and red reflective stripes attached to the side of the cars, encoding a six-digit company identifier and a four-digit car number. Light reflected off the colored stripes was read by photomultiplier vacuum tubes.
The Boston and Maine Railroad tested the KarTrak system on their gravel cars in 1961. The tests continued until 1967, when the Association of American Railroads (AAR) selected it as a standard, Automatic Car Identification, across the entire North American fleet. The installations began on 10 October 1967. However, the economic downturn and rash of bankruptcies in the industry in the early 1970s greatly slowed the rollout, and it was not until 1974 that 95% of the fleet was labeled. To add to its woes, the system was found to be easily fooled by dirt in certain applications, which greatly affected accuracy. The AAR abandoned the system in the late 1970s, and it was not until the mid-1980s that they introduced a similar system, this time based on radio tags.
The railway project had failed, but a toll bridge in New Jersey requested a similar system so that it could quickly scan for cars that had purchased a monthly pass. Then the U.S. Post Office requested a system to track trucks entering and leaving their facilities. These applications required special retroreflector labels. Finally, Kal Kan asked the Sylvania team for a simpler (and cheaper) version which they could put on cases of pet food for inventory control.
Computer Identics Corporation In 1967, with the railway system maturing, Collins went to management looking for funding for a project to develop a black-and-white version of the code for other industries. They declined, saying that the railway project was large enough, and they saw no need to branch out so quickly.
Collins then quit Sylvania and formed the Computer Identics Corporation.[9] As its first innovations, Computer Identics moved from using incandescent light bulbs in its systems, replacing them with helium–neon lasers, and incorporated a mirror as well, making it capable of locating a barcode up to several feet in front of the scanner. This made the entire process much simpler and more reliable, and typically enabled these devices to deal with damaged labels, as well, by recognizing and reading the intact portions.
Computer Identics Corporation installed one of its first two scanning systems in the spring of 1969 at a General Motors (Buick) factory in Flint, Michigan.[9] The system was used to identify a dozen types of transmissions moving on an overhead conveyor from production to shipping. The other scanning system was installed at General Trading Company's distribution center in Carlstadt, New Jersey to direct shipments to the proper loading bay.
Universal Product Code In 1966, the National Association of Food Chains (NAFC) held a meeting on the idea of automated checkout systems. RCA, who had purchased the rights to the original Woodland patent, attended the meeting and initiated an internal project to develop a system based on the bullseye code. The Kroger grocery chain volunteered to test it.
In the mid-1970s, the NAFC established the Ad-Hoc Committee for U.S. Supermarkets on a Uniform Grocery-Product Code to set guidelines for barcode development. In addition, it created a symbol-selection subcommittee to help standardize the approach. In cooperation with consulting firm, McKinsey & Co., they developed a standardized 11-digit code for identifying products. The committee then sent out a contract tender to develop a barcode system to print and read the code. The request went to Singer, National Cash Register (NCR), Litton Industries, RCA, Pitney-Bowes, IBM and many others. A wide variety of barcode approaches was studied, including linear codes, RCA's bullseye concentric circle code, starburst patterns and others.
In the spring of 1971, RCA demonstrated their bullseye code at another industry meeting. IBM executives at the meeting noticed the crowds at the RCA booth and immediately developed their own system. IBM marketing specialist Alec Jablonover remembered that the company still employed Woodland, and he established a new facility in Raleigh-Durham Research Triangle Park to lead development.
In July 1972, RCA began an 18-month test in a Kroger store in Cincinnati. Barcodes were printed on small pieces of adhesive paper, and attached by hand by store employees when they were adding price tags. The code proved to have a serious problem; the printers would sometimes smear ink, rendering the code unreadable in most orientations. However, a linear code, like the one being developed by Woodland at IBM, was printed in the direction of the stripes, so extra ink would simply make the code "taller" while remaining readable. So on 3 April 1973, the IBM UPC was selected as the NAFC standard. IBM had designed five versions of UPC symbology for future industry requirements: UPC A, B, C, D, and E.
NCR installed a testbed system at Marsh's Supermarket in Troy, Ohio, near the factory that was producing the equipment. On 26 June 1974, Clyde Dawson pulled a 10-pack of Wrigley's Juicy Fruit gum out of his basket and it was scanned by Sharon Buchanan at 8:01 am. The pack of gum and the receipt are now on display in the Smithsonian Institution. It was the first commercial appearance of the UPC.
In 1971, an IBM team was assembled for an intensive planning session, threshing out, 12 to 18 hours a day, how the technology would be deployed and operate cohesively across the system, and scheduling a roll-out plan. By 1973, the team were meeting with grocery manufacturers to introduce the symbol that would need to be printed on the packaging or labels of all of their products. There were no cost savings for a grocery to use it, unless at least 70% of the grocery's products had the barcode printed on the product by the manufacturer. IBM projected that 75% would be needed in 1975. Yet, although this was achieved, there were still scanning machines in fewer than 200 grocery stores by 1977.
Economic studies conducted for the grocery industry committee projected over $40 million in savings to the industry from scanning by the mid-1970s. Those numbers were not achieved in that time-frame and some predicted the demise of barcode scanning. The usefulness of the barcode required the adoption of expensive scanners by a critical mass of retailers while manufacturers simultaneously adopted barcode labels. Neither wanted to move first and results were not promising for the first couple of years, with Business Week proclaiming "The Supermarket Scanner That Failed" in a 1976 article.
On the other hand, experience with barcode scanning in those stores revealed additional benefits. The detailed sales information acquired by the new systems allowed greater responsiveness to customer habits, needs and preferences. This was reflected in the fact that about 5 weeks after installing barcode scanners, sales in grocery stores typically started climbing and eventually leveled off at a 10–12% increase in sales that never dropped off. There was also a 1–2% decrease in operating cost for those stores, and this enabled them to lower prices and thereby to increase market share. It was shown in the field that the return on investment for a barcode scanner was 41.5%. By 1980, 8,000 stores per year were converting.
Sims Supermarkets were the first location in Australia to use barcodes, starting in 1979.
Business Benefits of Barcodes[6]
Barcodes were developed to improve the speed of sales transactions, but there are other potential benefits to businesses, including:
- Better accuracy - Relying on a barcode to process data is far more accurate than relying on manually-entered data, which is prone to errors.
- Data is immediately available - Because of the processing speed, information about inventory levels or sales is available in real time.
- Reduced training requirements - Thanks to the simplicity of the barcode scanner, employees need little in the way of training in how to use it. Additionally, thanks to barcodes, there is much less for employees to have to learn and retain.
- Improved inventory control - Being able to scan and track inventory yields a much more accurate count, as well as a better calculation of inventory turn. Companies can hold less inventory when they know how soon they will need it.
- Low cost implementation - Generating barcodes is quick and easy, as is installing a barcode system. Potential savings can be realized almost immediately.
References
- ↑ Defining Barcode Lightspeed
- ↑ The Technical Definition of Barcode Barcodes Inc.
- ↑ Barcode Formats Cognex
- ↑ What are the Components of a Barcode Denso Wave
- ↑ Historical background of Barcodes Wikipedia
- ↑ What are the Business Benefits of Barcodes? [1]