Common Data Security Architecture (CDSA)
Definition of Common Data Security Architecture (CDSA)
Common Data Security Architecture (CDSA) is a set of layered security services and cryptographic framework that provide an infrastructure for creating cross-platform, interoperable, security-enabled applications for client-server environments. CDSA covers all the essential components of security capability, to equip applications for electronic commerce and other business applications with security services that provide facilities for cryptography, certificate management, trust policy management, and key recovery.[1]
CDSA was originally developed by Intel Architecture Labs and was released to the OpenSource community in May 2000. HP's CDSA implementation is based on the Intel V2.0 Release 3 reference platform, which implements CDSA V2.0 with Corrigenda, as defined in The Open Group's Technical Standard C914, May 2000. Starting with Version 7.3-1, HP provides CDSA as part of the OpenVMS Alpha operating system. CDSA is compatible with OpenVMS Alpha Version 7.2-2 and higher. CDSA provides a stable, standards-based programming interface that enables applications to access operating system security services. With CDSA, you can create cross-platform, security-enabled applications. Security services, such as cryptography and other public key operations, are available through a dynamically extensible interface to a set of plug-in modules. These modules can be supplemented or changed as business needs and technologies evolve. CDSA is security middleware that provides flexible mix-and-match solutions across a variety of applications and security services. CDSA insulates you from the issues of incorporating security into applications, freeing you to focus on the applications themselves. The security underpinnings are transparent to the user.[2]
CDSA Features[3]
CDSA is primarily a middleware framework that provides a set of APIs for creating and delivering secure applications. It allows application developers to easily add a set of different security features and services that have been prewritten and designed for client/server-based applications. CDSA provides the following features:
- Cryptography and encryption
- Certificate creation and management
- Policy management
- Authentication and non-repudiation
- Public key infrastructure
CDSA Layers[4]
CDSA is made up of three basic layers:
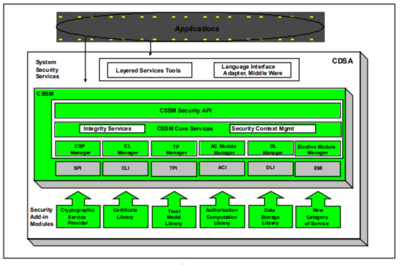
- System Security Services
- The Common Security Services Manager (CSSM)
- Security Add -in Modules
- System Security Services: System Security Services are bet ween applications and CSSM services. Software at this layer provides a high-level abstraction of security services such as secure e-mail, secure file systems, or secure communications. Applications can invoke the CSSM APIs directly, or use these layered services t o access security services on a platform.
- The Common Security Service Manager (CSSM): CSSM provides a set of core services that are common to all categories of security services. CSSM defines five basic categories of services:
- Cryptographic Service Provider (CSP) modules: CSPs perform cryptographic operations such as bulk encrypting, digesting, and digital signatures.
- Trust Policy (TP) modules: TPs implement policies defined by authorities and institutions and set the level of trust required to carry out specific actions (such as issuing a check or gaining access to confidential intellectual property).
- Certificate Library (CL) modules: CLs manage certificates and revocation list s, and access t o remote signing capabilities such as Certification Authorities (CA).
- Data Storage Library (DL) modules: DLs provide stable storage for security-related data objects, including certificates cryptographic keys and policy objects.
- Authorization Computation (AC) modules: ACs define a general authorization evaluation service that computes whether a set of credentials and samples are authorized to perform a specific operation on a specific object.
- Elective (EM) Modules: EMs add new and compelling security features not encompassed by the current set of service modules. For example one new feature that vendors might add to CDSA is a biometrics authentication. In addition, CSSM provides two additional core services:
- Integrity Services: The integrity services are used by CSSM itself to verify and guarantee the integrity of all the other components within the CSSM environment
- Security Context Management: CSSM provides context management functions (such as session information) to facilitate applications to utilize the security services
- Security Add-in Modules: This layer is made up of service provider modules that offer basic components — cryptographic algorithms, base certificate manipulation facilities, and storage etc.
See Also
Security Architecture
Security Policy
Security Reference Model (SRM)
Information Security Governance
Information Security
Adaptive Security Architecture (ASA)
Business Model for Information Security (BMIS)
Cognitive Security
Federal Information Security Management Act (FISMA)
Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS)
Computer Security
Enterprise Information Security Architecture (EISA)
Fault Configuration Accounting Performance Security (FCAPS)
Graduated Security
Information Systems Security (INFOSEC)
Mobile Security
Network Security
Cyber Security
References
- ↑ Definition - What Does Common Data Security Architecture (CDSA) Mean? The Open Group
- ↑ Understanding CDSA HPE
- ↑ CDSA Features Techopedia
- ↑ CDSA Layers GIAC