Global Management Accounting Principles (GMAPs)
Global Management Accounting Principles (GMAPs) are a set of statements that describe the fundamental values, qualities, norms and features to which management accounting professionals should aspire and that represent best practice.
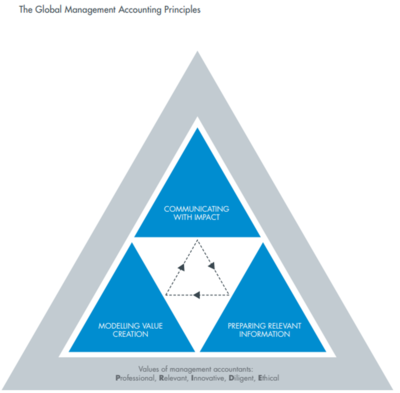
There are three major Principles, underpinned by the professional values of management accountants, as shown in Figure below
1. Preparing relevant information
Objective – To ensure that organisations plan for their information needs when creating tactics for execution.
This involves the identification, collection, validation, preparation and storage of information. It requires achieving an appropriate balance between:
- past, present and future-related information
- internal and external information
- financial and non-financial information.
2. Modelling value creation
Objective – To simulate different scenarios that demonstrate the cause-and-effect relationships between inputs and outcomes.
This requires a thorough understanding of the business model and wider macro-economic environment. It involves the analysis of information along the value creation path, the evaluation of opportunities within this context, and a focus on the risks, costs and value of opportunities.
3. Communicating with impact
Objective – To drive better decisions about strategy execution at all levels.
This involves communicating the results of scenario analysis in a manner that is tailored to the decision being considered as well as to the decision-makers (or other audiences). It requires breaking down complexity and transparency about how conclusions have been reached.[1]
- ↑ The three major principles of GMAPs CIMA Global