Human Resources Information System (HRIS)
A Human Resources Information System (HRIS) is a software or online solution that is used for data entry, data tracking and the data information requirements of an organization's human resources (HR) management, payroll and bookkeeping operations. A HRIS is usually offered as a database. HRIS is geared toward enhancing the capacity of HR management to:
- Absorb new and promising technologies
- Simplify workflow
- Optimize precision, stability and credibility of workforce data
- Simplify the deployment and collection of data[1]
A HRIS generally should provide the capability to more effectively plan, control and manage HR costs; achieve improved efficiency and quality in HR decision making; and improve employee and managerial productivity and effectiveness. A HRIS offers HR, payroll, benefits, training, recruiting and compliance solutions
Most are flexibly designed with integrated databases, a comprehensive array of features, and powerful reporting functions and analysis capabilities that you need to manage your workforce. This can give back hours of the HR administrator’s day previously spent attending to routine employee requests.[2]
Components of HRIS[3]
Explained below are the various components of the HRIS.
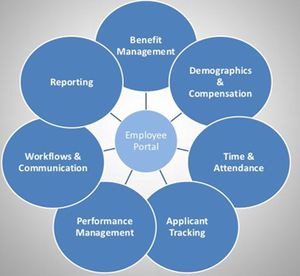
- Database: HRIS core offering includes a database to store employee information. HR professionals can input all personnel data into the system which can be accessed from anywhere, round the clock. Types of data that HR professionals collect in the database include compensation history, emergency contact information, and performance review. The core database can also be viewed as an online backup for paper files.
- Time and Labour Management: Activities like time and labour management can highly time consuming. HRIS package allows employees to input their own hours worked and allows managers to immediately verify vacation requests, and the data is directly fed to the payroll. Time and labour management also improves the HR department’s ability to track punctuality and attendance.
- Payroll Function: Payroll function is yet another major component of a HRIS model. HR can easily download or unload employee hours, and issue cheques or payroll deposits to employees. Salaried employees can also be paid with substantially reduced risk of errors. The HRIS payroll software usually improve tax compliance for locations with multiple tax levels.
- Benefits: Some HRIS employers allow employers to establish and maintain medical benefits and retirement investments through their software. Such applications allow employers to have one-stop shopping experience for all their human resources data management needs. Other HRIS packages facilitate medical benefits and retirement investment deductions for payroll but not the establishment of those benefits.
- Employee Interface: Most HRIS packages allow for an employee to have limited user access. Employee users access a part of the database where they can update their personal information, review pay scales, change retirement benefit programs, update direct deposit information or download benefit election documents.
- Recruitment and Retention: Finally, it can be said that recruitment and retention are the most important components of HRIS. It goes without saying that it is the anchor of all HR policies and systems. Finding new talent, acquiring them, keeping them engaged and finally being able to retain them are the major task of a HR person. HRs also have to ensure that employees are not only able to do their work, but they are also provided with the required training; receives proper compensation and benefits from the organization.
source: Medium
Solutions offered by HRIS Systems[4]
There are a number of solutions offered to a company that adopts a HRIS. Some of these include solutions in training, payroll, HR, compliance, and recruiting. The majority of quality HRIS systems include flexible designs that feature databases that are integrated with a wide range of features available. Ideally, they will also include the ability to create reports and analyze information quickly and accurately, in order to make the workforce easier to manage. Through the efficiency advantages conferred by HRIS systems, a HR administrator can obtain many hours of his or her day back instead of spending these hours dealing with non-strategic, mundane tasks required to run the administrative-side of HR. Similarly, a HRIS allows employees to exchange information with greater ease and without the need for paper through the provision of a single location for announcements, external web links, and company policies. This location is designed to be centralized and accessed easily from anywhere within the company, which also serves to reduce redundancy within the organization. For example, when employees wish to complete frequently recurring activities such as requests for time off or electronic pay stubs and changes in W-4 forms—such procedures can be taken care of in an automated fashion without the need for human supervision or intervention. As a result, less paperwork occurs and approvals, when deigned, may be appropriated more efficiently and in less time.
Who uses HRIS and how is it used?[5]
Contemporary HRIS must be versatile enough to meet the needs of multiple organization stakeholders. HRIS is commonly used by HR professionals as well as by managers in functional areas. All have different needs for the information provided by a central data system.
- HR Professionals
- Reporting and compliance
- Payroll and compensation analysis
- Benefits administration
- Applicant tracking, skills inventory
- Functional Managers
- Performance management and appraisal
- Recruitment and resume processing
- Team and project management
- Training and skills testing
- Management development
- Individual Employees
- Self-service benefit options
- Career planning
- Training and development
Product Selection Criteria: Pre-HRIS and Post-HRIS[6]
Pre-HRIS
When implementing a Human Resources Information System, there are a number of selection steps and criteria. The most important ones are listed below.
- Price scoping of competing products
- Functionality scoping, including the specifics of reporting and metrics of competing products
- Vendor record & reputation analysis
- User and data security protocols/ compliance required
- Deep evaluation of Customization and third-party integration of competing products
- Cost/time investment for the entire implementation lifecycle
- Post implementation support required
Post-HRIS
SIPOC mapping is a term from the Six Sigma discipline. It refers to Supplier, Input, Process, Output, and Customer. If we relate this to the HRIS implementation process, we get the following picture.
- Supplier: HRIS Vendor, Implementation consultants, Third party integration consultants, compliance consultants
- Inputs: HRIS implementation process, Application of expertise, Customization & Third party integration, Beta testing
- Process: The process refers to the operational process of the HRIS, as described above
- Outputs: Implemented HRIS, Fully trained Staff, Workflow Digitalization, Workflow automation, Improved HR Efficiency
- Customer: HR department, employees, Other organizational stakeholders, Competitive leverage of the organization
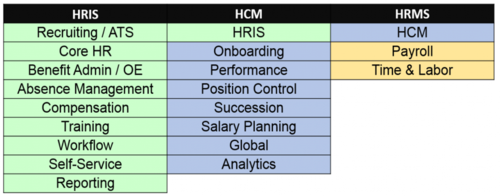
HRIS vs. HCM vs. HRMS[7]
The HRIS vs. HCM vs. HRMS chart below shows the major functional differences between the three acronyms and what functionality that should be associated with each.
source: HRMS Solutions
HRIS Security and Privacy[8]
An HRIS also helps secure employee data and keep information private. When using paper forms or spreadsheets, information can easily be accessed by people who may not have the authority to access it. An HRIS can secure information so that it can only be accessed by the individuals that need to have access to it. Data security and privacy are important factors when handling sensitive personal information, especially in countries like Germany or France, where works councils have a strong role in protecting employee data. With the exception of lock and key, protecting paper records can be extremely difficult.
Benefits of the Right HRIS[9]
An effective HRIS provides information on just about anything the company needs to track and analyze about employees, former employees, and applicants.
- It's fairly inexpensive to implement a basic HRIS, but make sure whatever you implement meets your company's actual needs. Do you want to be able to run turnover reports? Post organizational charts?
- Allow managers to electronically access previous performance appraisals? Do you want everything to have to be done through the HR department or would you like managers to access the information themselves?
- With an appropriate HRIS, Human Resources staff enable employees to do their own benefits updates and address changes, thus freeing HR staff for more strategic functions. Additionally, data necessary for employee management, knowledge development, career growth and development, and equal treatment is facilitated.
- Finally, managers can access the information they need to legally, ethically, and effectively support the success of their reporting employees. They can run their own reports and enter plans into the system to help with succession.
See Also
- Human Resource Management (HRM)
- Human Capital Management (HCM)
- Human Resources Analytics (HR Analytics)
- Performance Management
- Applicant Tracking System (ATS)
- Personnel Management
References
- ↑ Definition - What does Human Resources Information System (HRIS) mean? -Techopedia
- ↑ What is Human Resources Information System (HRIS)? -Dresser Associates
- ↑ Components of HRIS -Medium
- ↑ Solutions offered by HRIS Systems -HR Payroll Systems
- ↑ Who uses HRIS and how is it used? -SHRM
- ↑ Pre-HRIS and Post-HRIS Product Selection Criteria -AIHR
- ↑ HRIS vs. HCM vs. HRMS -HRMS Solutions
- ↑ HRIS Security and Privacy -Techtarget
- ↑ Benefits of the Right HRIS -thebalancecareers
Further Reading
- How to Successfully Select and Implement an HRIS -AnalyticsHR
- Human Resource Information Systems (HRIS) in HR Planning and Development in Mid to Large Sized Organizations -Asha Nagendra,Mohit Deshpande
- Antecedents and outcomes of human resource information system (HRIS) use -Normalini Md. Kassim, T. Ramayah, Sherah Kurnia
- What does it take to implement Human Resource Information System (HRIS) at scale? Analysis of the Expected Benefits and Actual Outcomes -Aizhan Tursunbayeva, Claudia Pagliari, Raluca Bunduchi, Massimo Franco
- Human resource information systems: a review and empirical analysis -E.W.T. Ngai, F.K.T. Wat
