Product Portfolio
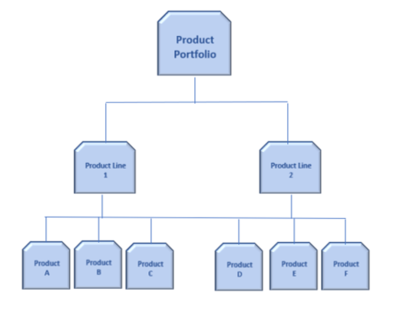
Product Portfolio is a set of all products, product lines or other groupings within a business unit or business division. Products can include existing products, which may be at various phases of their own life cycles, as well as incoming products (those anticipated, actually in development, or in the launch phase). In smaller organizations, a single product or product line may in fact comprise the entire portfolio.
Common approaches to organize products are:
- Organize by markets on which the products focus
- Organize by types of products produces
- Broad functions; themes of the products or the precise needs of the market being met by those products and how diverse are those needs
- e.g. if GE produces am light bulb and a tube light - they can be put in the same portfolio
- However, if GE also produces medical devices or has financial services division with financial products - which will have to be in their own portfolio independently
- Types of development methods used to produce[1]
Typically, product portfolios are dynamic: there are products at different stages of development across the product lifecycle; new product ideas that are added; and some products that fail and are subsequently removed from the portfolio.
Understanding Product Portfolios[2]
Product portfolios are an important element of financial analysis because they provide context and granularity to a firm and its primary operations. Investors can distinguish between long-term value stocks and short-term growth opportunities. Portfolio analysis of a firm's product offerings also allows investors to nail down specific drivers of financial performance, which is necessary for effective modeling.
The various components of a portfolio also face different market dynamics and can contribute inconsistently to the bottom line. A firm's market share can vary among the parts of its offering, with more dominant products generally requiring different strategies than high-growth portions of the portfolio. A shifting sales mix can have significant consequences for the bottom line when margins vary across the portfolio.
Companies often re-brand or restructure underperforming and unprofitable products, a strategy that requires portfolio analysis. Products that contribute the most income are generally the most important for short-term financial analysis, and alterations to these flagship elements of the portfolio impact performance more substantially.
Importance of Products Portfolio to Businesses[3]
1) Product Innovation: It is very important to follow the strategy of having a Product Portfolio and analyzing it in the regular intervals in order to plan and come up with the new and innovative line of products to be offered to the target market. It helps in defining the types and nature of products that are liked and preferred by the customers and with the experience and knowledge, launch the new line of products that are not only innovative and novel in ideation but matches the taste and preferences of the target market.
2) Tax Benefits: Managing and analyzing the Product Portfolio on the regular basis helps to structure the investments and all the other financial elements of the company resulting in the various tax benefits.
3) Aligns projects with the businesses strategy: It is very important that the product offerings and their revenue generations match and align with the long-term vision of the company and the business strategy. As then only the company will be able to accomplish its aims and objectives of higher sales, elevated profits, competitive advantage, and increased market share. Having the proper management of the Product Portfolio helps the management to align the existing and projects in the pipeline with the overall business strategy and vision of the company.
4) Visualize the entire products-line: Studying and analyzing the operations, revenue generation, and other facets of each and every product on an individual level offered by the company can be very cumbersome and will not help to draw comparative study effectively. But with the Product Portfolio in place, all the key members of the management are able to visualize the entire portfolio of the all the old, existing, and future products having a broader spectrum.
5) Effective allocation of resources: Having and managing the Products Portfolio helps in allocating the various resources of the firm such as finances, human resources, and manufacturing plants amongst others in an effective manner. It helps in figuring out the products that are working as the cash cows for the companies, the products that are capable for higher market share but require the boost from the management, and the products that are redundant in nature and needs to be taken off from the market.
6) Data for the key members of the management: It helps providing the crucial and important data to the key members of the management that enlightens them about the performance of the products in the market, revenue generation by the each product, market share, customer preferences, and requirement of any sort of tweaking or innovation in any products amongst others that helps with the planning and execution of the next plans and strategies of the business.
7) Cash flow: The company requires the regular flow of cash for the day to day business operations such as paying overheads, staff salaries, and more along with the money required for the investments in the existing and future line of the products. And with the proper planning and administration of the Products Portfolio, the cash flow issues of the company are sorted out as it helps to determine the products that bring the maximum revenues and the company will allocate the maximum resources on the same.
8) Synergy within the internal team: All the products offered by the company and their operations are not managed by the single person, but they are managed by various departments and individual teams formulated by the management of the firm. This case is mainly applicable to the large corporate firms that have a huge and varied line of products in the market. And with the proper Products Portfolio in place, there are various team meetings and discussions resulting in all the members on the same page and well aware about the overall business strategy and operations of the firm having a required synergy to attain the long-term business aims and objectives.
9) Proper selection of the target industry: Products Portfolio helps the management to figure out on why the certain lines of products are performing extremely well working as the cash cows for the firm whilst some of them not matching the required and envisioned plans and objectives. And if the later is having the issue of the products not targeted and promoted to the required target market and audience, the elements, and strategies of the Products Portfolio helps to iron out this problem.
Product Portfolio Examples[4]
A product portfolio is the complete collection of products or services that a business sells. The portfolio may be straightforward and consist of a single product, or it may consist of multiple, diversified product lines.
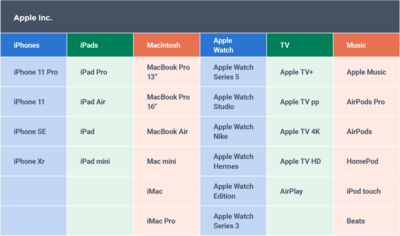
Larger organizations, such as Apple Inc., organize similar products into product lines or product families. The Macintosh product line includes the MacBook, MacBook Pro, MacBook Air, Mac Mini, iMac, and Mac Pro. However, the entire Apple product portfolio is much more complicated, comprising six product lines and numerous products within each line. The chart below shows the entire Apple product portfolio, arranged by product line.
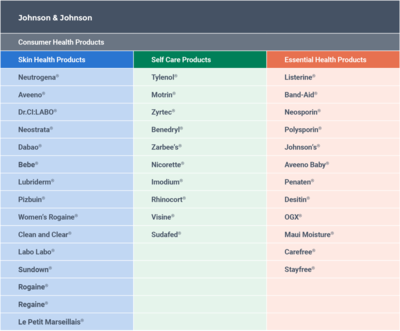
Johnson & Johnson is another multifaceted organization, with a product portfolio that spans consumer health products, medical devices, and pharmaceuticals. Each of those categories breaks down further into household name brands. Johnson & Johnson’s consumer health product line alone consists of over 35 individual product brands.
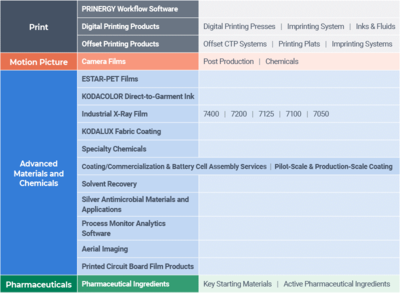
Another well-known brand, Eastman Kodak, founded in 1888 by George Eastman and Henry A. Strong, held the dominant position in the film photography market for most of the twentieth century. The advent of digital photography left behind Kodak’s primary business, analog photography. However, the company continues to thrive today, with a focus on printing products. Recently, Kodak began conducting an internal review in connection with the potential diversification into pharmaceuticals.
Theoretically, what might the Kodak product portfolio look like when the company launches the Kodak pharmaceutical branch? The Kodak team will likely make product portfolio analysis part of its internal review, so it can determine how pharmaceuticals fit into the company’s portfolio. That product portfolio analysis will also ascertain whether or not it is profitable to maintain all product lines and products.
Building a Product Portfolio Roadmap[5]
A product portfolio roadmap is a high-level visual representation of what products the organization should invest in developing over a particular time horizon, and, crucially, why. It is important to keep in mind that a product portfolio is dynamic because the organization is continually changing. Therefore, the roadmap must be regularly assessed and adapted, i.e. active.
Having a product portfolio roadmap is a significant artefact to support communication and consensus-building in the organization, but it is from the process of developing the roadmap that the organization gains the most value. The process or action of developing the roadmap prompts and invokes many important questions.
- What challenges are we solving?
- What objectives should we meet to address these challenges?
- What capabilities do we need to deliver in order to meet the objectives?
- What actions are required to bridge the capability gaps?
- What products do we need to bridge the capability gaps?
- Which products are the higher priority?
- Which products should we invest in delivering and in what order over time?
Answering these questions is essential to a good product portfolio roadmap. The visual roadmap is only one small output of the process; the insights and decisions made are the true gems of having a roadmap.
Follow a simple and consistent method that aligns your portfolio of products to your organization’s capability gaps, objectives and challenges, i.e. you need to understand the ‘why’, analyze the ‘what’ and then you can visualize the ‘how’.
See Also
- Product
- Product-as-a-Service (PaaS)
- Product/Market Fit
- Product Data Management (PDM)
- Product Design
- Product Development
- Product Information Management (PIM)
- Product Life Cycle
- Product Lifecycle Management
- Product Management
- Product Personalization
- Product Portfolio Management
References
- ↑ Definition - What Does Product Portfolio Mean? ProductLeaders.org
- ↑ Understanding Product Portfolios Investopedia
- ↑ What is the importance of Products Portfolio to businesses? Marketing91
- ↑ Company Product Portfolio Examples Smartsheet
- ↑ Four Steps for Building a Product Portfolio Roadmap Jibility