Product Portfolio Management
Definition - What is Product Portfolio Management?
Product Portfolio Management (PPM) is a definitive process of analyzing and assessing each product and its current level of success. It also involves identifying risks and future opportunities, streamlining resource allocation based onproduct success and priority, and ultimately aligning these products with the business’s long-term strategic goals. This methodology enables product managers and stakeholders to constantly review their products, improve them based on evolving consumer demands, add more products or services and streamline the product execution based on resource capacity. These processes cumulatively result in an increased Return on Investment, thereby enhancing the business’s top line.[1]
source: Rick Steinbrenner
Product Portfolio Management Approaches[2]
These are some common axes that used to define and shape a product portfolio mix:
- Investment versus Market/Technical Risks (most common)
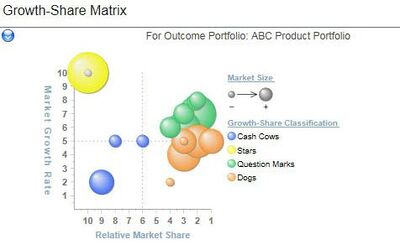
- Market Growth versus Market Share (second most common)
- Revenue or Profit versus Strategic Alignment
- Competitive Position versus Market Maturity
- Industry Attractiveness versus Competitive Strengths
If you are applying the most common approach — a risk-based approach, a company might allocate its investments into three categories:
- Core Products: A core product introduces a modification of an existing offering to create a new product or new product line. Often this core product has the highest market share and often delivers the most to the bottom line. Core products are sold to existing customers and leverage existing product technologies. Typically, they have the highest resource allocation in the product portfolio.
- Adjacent Products: Adjacent products are conceptually and functionally the same as core products, but they serve a market that is new to the company. Or they may consist of a substantial modification to a product, expanding the market the company has already entered. These are often variants or derivative products from an existing product line.
- Transformational Products: Transformational products innovate in products and markets simultaneously. They may involve a ground-up design or a new-to-the-world product. They often include dramatic improvement in functionality or performance.
Leveraging Technology for Product Portfolio Management[3]
Product Portfolio Management can be implemented across the enterprise. An automated solution breaks down silos, providing an unprecedented line of sight across geographies, brands and teams to understand product performance, the NPD pipeline, team productivity, potential roadblocks, ongoing realization of the corporate strategy and other areas. Powerful analysis, reporting and dashboard capabilities within these solutions provide full transparency, with real-time analytics to inform decisions about product priorities and resource allocation in various scenarios. In-flight work of all types can be monitored and managed across teams, departments, business units and regions. With better insight into pipeline bottlenecks and other problem areas, you can quickly and proactively pivot and see immediate results.
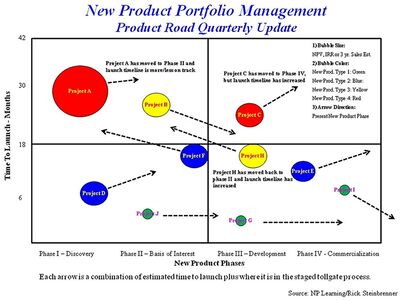
A Product Portfolio Management solution can enable and automate industry best practices, templates and visual workflows for project execution and can provide a structure for analyzing product portfolios, including scoring methods, X-Y graphs, the growth-share matrix and bubble diagrams. Product roadmaps can be created and maintained to communicate goals, timelines, priorities, dependencies and other critical information. These powerful tools can eliminate cumbersome spreadsheets and manual processes. More importantly, they centralize the product data and provide a single source of truth. As a result, decisions are based on accurate, real-time analytics instead of gut reactions.
A centralized solution streamlines communication and removes barriers to collaboration, so teams can be more productive. The ability to trust the numbers and each other becomes crucial when under-performing products are on the chopping block. A product planning framework is in place to assign relative values and priorities within the context of the entire portfolio. Your team can work together to weigh KPIs against strategic objectives, and cull low-value products before they drain your resources. Combining these capabilities into one purpose-built system is what helps achieve a higher success rate for higher-value products.
Product Portfolio Management Vs. Product Management[4]
A product portfolio manager’s responsibilities differ significantly from those of a product manager. While product managers focus on specific products, product portfolio managers are responsible for portfolios of products.
- Product Manager: Usually responsible for a single specific product, its features, product roadmap, and broader strategy.
- Product Portfolio Manager: Responsible for an organization’s portfolio of products, their inter-relationships, and the portfolio’s role in the market.
To illustrate the different responsibilities of these two roles, consider this. A product manager will focus on identifying additional features that could address the needs of a given product’s users. The product portfolio manager, by contrast, will focus on what other products the company might want to build to address the needs of these users.
Benefits of Product Portfolio Management[5]
Product portfolio management brings plenty of benefits to companies who make it a part of their business operations. Product portfolio management provides a centralized (rather than individual) view of an entire suite of products against the prevailing marketplace for those products. Unlike individual product management, a portfolio approach eliminates competing initiatives and agendas for product development. Decisions about resource allocation to strengthen products in growing markets are balanced against decisions on offerings that need improvement or can be eliminated. Practitioners view products through the dual prism of how they are performing against the real marketplace conditions. Product portfolio management also utilizes data-driven methods to streamline R&D by identifying products or markets with the best opportunities for new development, growth, and profitability. Effective product portfolio management initiatives will help:
- Bring new, innovative products to market quickly
- Improve agility and response to market conditions
- Reduce the time it takes to bring products to market
- Improve competitive positioning
- Maximize product investments
- Improve visibility into product mix and identify strong and weak products to clarify resource allocation
- Reduce risk and ensure that product investments align with business objectives
- Prioritize product focus
- Improve communication and collaboration
- Improve overall product management efficiency
See Also
- Product
- Product-as-a-Service (PaaS)
- Product/Market Fit
- Product Data Management (PDM)
- Product Design
- Product Development
- Product Information Management (PIM)
- Product Life Cycle
- Product Lifecycle Management
- Product Management
- Product Personalization
- Product Portfolio
References
- ↑ What Does Product Portfolio Management Mean? Saviom
- ↑ Product Portfolio Management Approaches TCGen
- ↑ How Technology Can Be for Product Portfolio Management Planview
- ↑ How Does Product Portfolio Management Differ from Product Management? Product Plan
- ↑ What are the Benefits of Product Portfolio Management? Smartsheet