Difference between revisions of "Business Function Model"
m |
m |
||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
== See Also == | == See Also == | ||
<div style="column-count:2;-moz-column-count:3;-webkit-column-count:3"> | <div style="column-count:2;-moz-column-count:3;-webkit-column-count:3"> | ||
| − | + | #[[Business Process Modeling|Business Process Modeling (BPM)]] | |
| − | + | #[[Organizational Structure]] | |
| − | + | #Functional Organizational Structure | |
| − | + | #[[Value Chain Analysis]] | |
| − | + | #[[Enterprise Architecture]] | |
| − | + | #[[Functional Strategy]] | |
| − | + | #[[Capability Maturity Model (CMM)]] | |
| − | + | #[[Business Operations]] | |
| − | + | #[[Business Capability]] | |
| + | #[[Business Model]] | ||
| + | #[[Business Strategy]] | ||
| + | #[[Business Objective]] | ||
| + | #[[Business Goals]] | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
Revision as of 10:57, 25 August 2023
A Business Function Model (BFM) is a general description or category of operations performed routinely to carry out an organization's mission. They "provide a conceptual structure for the identification of general business functions". It can show the critical business processes in the context of the business area functions. The processes in the business function model must be consistent with the processes in the value chain models. Processes are a group of related business activities performed to produce an end product or to provide a service. Unlike business functions that are performed on a continual basis, processes are characterized by the fact that they have a specific beginning and an end point marked by the delivery of a desired output. The figure on the right depicts the relationship between the business processes, business functions, and the business area’s business reference model.[1]
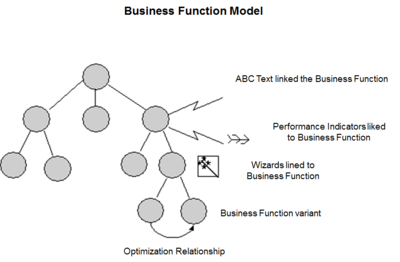
source: Infor
Stages in Business Function Modeling[2]
The stages in Business Function Modeling within IMM™ are:
- Identify sources of Functions or collect information from which Functions can be identified.
- Analyze all gathered information and sources and extract all “candidate” functions.
- Convert “Candidate” Functions to true Functions.
- Build the Function Catalogue.
- Feed back what has been modelled to the business to ensure that it is correct.
- Liaise with system developers to ensure that any systems built truly support the Function Catalogue.
The Function Catalogue is the single most powerful business model that there is because:
- It allows all of a business to be to be seen – on one sheet of paper if necessary.
- All decomposition can be done through it – painlessly.
- It enables duplication of activity to be identified and removed.
- All other models – including process models – are built from it.
- It suggests good structures for the business.
- It tells you what modules you need in any computer system.
- It is a powerful aid for planning computer development projects
See Also
References
- ↑ What is Business Function Model Wikipedia
- ↑ Stages in Business Function Modeling Integrated Modeling Method
