14 Principles Of Management
Henri Fayol proposed four primary functions of management and fourteen principles of management.[1] The principles of management refer to the fundamental truth which is generally applied to the everyday business operations for ensuring effective management of the organization. Though these principles are not very appropriate for the modern business world, they have laid the foundation of business management.
Functions of Management
- Planning
- Organizing
- Leading
- Controlling
Lately scholars of management combined the commanding and coordinating function into one leading function.
The 14 Principles of Management
- Division of labor - The division of work is the course of tasks assigned to, and completed by, a group of workers in order to increase efficiency. Division of work, which is also known as division of labor, is the breaking down of a job so as to have a number of different tasks that make up the whole. This means that for every one job, there can be any number of processes that must occur for the job to be complete.
- Authority - Managers must be able to give orders. Authority gives them this right. Note that responsibility arises wherever authority is exercised.
- Discipline - Employees must obey and respect the rules that govern the organization. Good discipline is the result of effective leadership.
- Unity of command - Every employee should receive orders from only one superior.
- Unity of direction - Each group of organizational activities that have the same objective should be directed by one manager using one plan for achievement of one common goal.
- Subordination - The interests of any one employee or group of employees should not take precedence over the interests of the organization as a whole.
- Remuneration - Workers must be paid a fair wage for their services.
- Centralization - Centralization refers to the degree to which subordinates are involved in decision making.
- Scalar chain - The line of authority from top management to the lowest ranks represents the scalar chain. Communications should follow this chain.
- Order - this principle is concerned with systematic arrangement of men, machine, material etc. there should be a specific place for every employee in an organization
- Equity - Managers should be kind and fair to their subordinates.
- Stability of tenure of personnel - High employee turnover is inefficient. Management should provide orderly personnel planning and ensure that replacements are available to fill vacancies.
- Initiative - Employees who are allowed to originate and carry out plans will exert high levels of effort.
- Esprit de corps - Promoting team spirit will build harmony and unity within the organization.<ref>Fayol's 14 principles of management then and now
Features of Principles of Management
The principles of management are identified facts which are developed through individual experiences and can be applied to all kinds of business entities. To know more about these principles, let us go through its following characteristics:
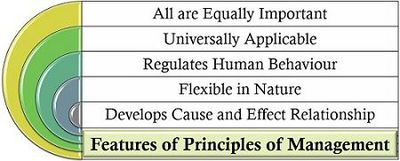
source: The Investors Book
- All are Equally Important: Every management principle holds equal importance in the business organization.
- Universally Applicable: These principles can be applied to any kind of organization, whether large or small or belongs to any industry.
- Regulates Human Behaviour: The application of the management principles helps the organization to monitor and control the behaviour of the personnel.
- Flexible in Nature: The applicability of these principles vary from organization to organization.
- Develops Cause and Effect Relationship: The principles of management establishes a relationship between every action and its consequences in the short and long run.
See Also
Management
Management Accounting
Management Buy-Out
Management Consulting
Management Development
Management Metaphors
Management Model
Management Style
Management Succession Planning
Management by Exception (MBE)
Management by Objectives (MBO)
Management by Wandering Around (MBWA)
IT Strategic Planning
e-Business Strategic Planning
Governance of Information Technology (ICT)
What is Enterprise Architecture Planning
Information Technology Sourcing (IT Sourcing)
Information Technology Operations (IT Operations)
Chief Information Officer (CIO)
Leadership
References
Further Reading
- Fayol's 14 principles of management then and now: A framework for managing today's organizations effectively Carl A. Rodrigues
