Gartner Business Value Model
The Gartner Business Value Model is a set of defined performance metrics that extends traditional accounting metrics. It is a set of the most common business outcomes resulting from IT investments and ongoing IT services. Each metric in the model is mathematically linked to the financial statements (that is, lagging indicators), providing an ability to simulate the impact of investments on financial results. It is useful tool that extends, not replaces, traditional accounting metrics in determining the real drivers of business value and in closing the measurement gap. The Gartner Business Value Model is all about information content and is targeted at providing senior business executives with the information they need to make better decisions. It designed to enhance IT-to-business communication by enabling greater precision and meaning in addressing increasingly complex business value creation issues and mechanisms (or economic architectures).[1]
The Business Value Model provides the common language necessary to bridge the gap between high-level strategic positions and the tactical activities necessary to make them happen. It does not replace standard financial metrics, it extends them. The Business Value Model adheres to the best practices for building a causal model. It is made up of leading indicators of financial results. The metrics are mutually exclusive and collectively exhaustive at a mid to upper management level, there are no more then 7 (+/- 2) metrics at any given management level and the relationships between the metrics (cause and effect) have been documented.
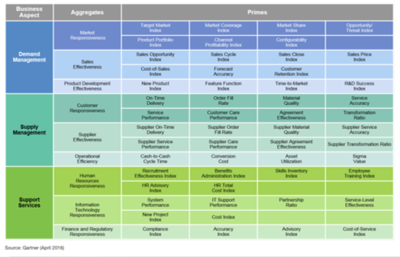
The activities measured fall into three broad groups:
- demand management
- supply management and
- support services management
They are further broken down into "aggregate measures." Each aggregate measure breaks down further into what we call prime measures. The figure below shows the prime measures for sales effectiveness. There are prime measures behind each of the other aggregates shown in the figure. This model is a tool that can be used to reduce the time and risk of identifying, building and managing an integrated set of activities necessary to execute a strategic position.
Guiding Principles of Business Value Model[2]<br />
The following principles were developed to guide the development of the Gartner Business Value Model:
- All metrics, when used collectively, are leading indicators of financial performance.
- No more than seven (plus or minus two) metrics are to be used at any given level.
- The metrics should be collectively exhaustive and mutually exclusive.
- The metrics should focus on the executive and middle management levels.
- The metrics should be based on standard prime metrics to foster collaboration and enable the comparison of
- The metrics should be based on standard prime metrics to foster collaboration and enable the comparison of internal and external entities.
- The metrics should be made flexible by an architecture that allows many combinations of standard and custom metrics.
- The holistic nature of the model should capture the cause-and-effect relationships between business functions.
- The metrics should be selected based on data available in automated business systems.
- The model should evolve and develop over time by adding and deleting metrics.
Applications of the Business Value Model[3]
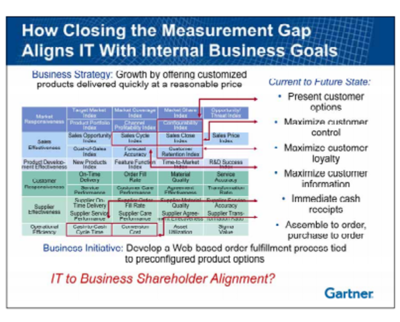
The following is an example of how to use performance metrics to identify the activities necessary to optimize the business strategy. In this example, the business executives have identified a strategic position to exploit unmet consumer demand for customized products with quick delivery and at a reasonable price. In the example in the figure below, the Business Value Model is used to identify activities that support this strategic position. Marketing and sales activities are selected to focus on consumer needs and ways of engaging them. Operational activities are selected to ensure profitability at a reasonable price. Using the metric definitions, data can be collected on each of these activities to baseline performance. Then the management team can begin to look for ways of improving performance in each of the activities selected. Process improvements enabled by technology as well as organizational changes can be identified and form the basis of a list of candidate objectives. The management team then estimates the targeted improvements to the performance measures selected, resulting from various combinations of candidate objectives. These targeted improvements are translated into financial results using the relationship documented in the Business Value Model. This approach reduces the time and risk of identifying an integrated set of activities that optimizes execution of the strategy. It also provides business executives and their management teams with a way to monitor progress objectively
See Also
Gartner's Hype Cycle Methodology
Gartner's PACE Layered Application Strategy
Gartner Business Value Model
Gartner Magic Quadrant
Gartner's MarketScopes
Gartner Vendor Rating
Gartner Market Forecast
Gartner's Market Share Analysis
References
- ↑ Definition - What is the Gartner Business Value Model Gartner
- ↑ The principles that were developed to guide the development of the Gartner Business Value Model Michael Smith
- ↑ What are the applications of the Business Value Model? Michael Smith