Strategic Planning Cycle
The strategic planning cycle embodied in a set of formal planning procedures, ensures that managers examine major strategic issues, or 'strategic elephants', faced by their organization. This is necessary to overcome the natural preoccupation with short term operational problems. The formal planning cycle also provides a logical framework to enable managers to tackle their strategic elephants in a systematic way, and so ensure that no major issues are left unaddressed.[1]
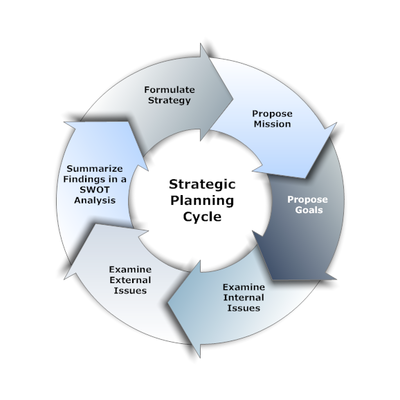
Although the strategic planning process may be different for businesses, a Visual Strategic Planning process is modeled off of the Strategic Planning cycle (see figure below) , where the steps are followed in this order:
- Propose mission - The first thing that a company will need to do in the planning process will be to propose a mission. Also known as mission statements, missions outline the unchanging values and purpose of the firm in addition to the forward-looking visionary goals that are an integral part of the pursuit of future opportunities. When the values and purpose of the company are combined with the visionary goals, they form the company’s business vision. Company leaders can use the business vision to make reasonably attainable financial and strategic objectives. Financial objectives can include such things as sales targets, earnings growth, and debt or loan repayment. Strategic objectives can be things such as market share and reputation.
- Propose goals - After the company has proposed and established their mission, they are free to propose goals that they want to reach. These goals may include things like establishing a solid customer base, perfecting marketing techniques, creating a loyalty or rewards program, or expansion timelines.
- Examine internal issues - The next step for companies to take after proposing their goals is to examine internal issues that could affect the company’s performance. After these issues have been identified, management can choose which issues they will focus the strategic plan on.
- Examine external issues - In addition to internal barriers to success, the company will also need to examine external issues that could affect their chances of surviving. Examples of external issues that could affect the survivability of the company are regulation changes and the needs of the client population changing.
- Summarize findings in a SWOT analysis - Define your company’s Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities and Threats (SWOT) that are involved in a business venture. During the SWOT Analysis consider your products, location and industry. Specify the objectives of your business venture and identify the factors that can affect your business.
- Formulate strategy - The final step in the creation of an effective strategic plan is to formulate a strategy for the company, with the strengths being as appropriately matched as possible with the opportunities that are available to the business, while taking time to address both the weaknesses of the business and the threats to it.[2]
source:SmartDraw
See Also
Strategic Management
Strategic Alignment Maturity Model
IT Value Mapping
Strategic Planning
Business Vision
Strategy
Business IT Alignment
Business Strategy
corporate strategy
IT Strategy Framework
IT Capability
Business Capability
References
- ↑ What is the Strategic Planning Cycle? Executive Consultancy Service
- ↑ Understanding the Strategic Planning Process Clint International
Further Reading
- Planning Cycle Graphics Ohlone College
- Strategic Planning Basics Balanced Scorecard
- The Planning Cycle - A Planning Process for Medium-Sized Projects Mindtools
- How to improve strategic planning McKinsey
- Strategic Planning Cycle (At a Glance) Prince Georges Community College
- Strategic Management: 3 Steps to the Cycle of Success CSSP
