Business Impact Analysis (BIA)
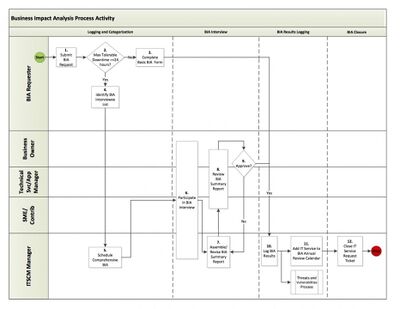
A business impact analysis (BIA) is the process of determining the criticality of business activities and associated resource requirements to ensure operational resilience and continuity of operations during and after a business disruption. The BIA quantifies the impacts of disruptions on service delivery, risks to service delivery, and recovery time objectives (RTOs) and recovery point objectives (RPOs). These recovery requirements are then used to develop strategies, solutions and plans.[1]
The BIA should identify the operational and financial impacts resulting from the disruption of business functions and processes. Impacts to consider include:
- Lost sales and income
- Delayed sales or income
- Increased expenses (e.g., overtime labor, outsourcing, expediting costs, etc.)
- Regulatory fines
- Contractual penalties or loss of contractual bonuses
- Customer dissatisfaction or defection
- Delay of new business plans[2]
source: UCSF
Purpose of a Business Impact Analysis[3]
Many organizations struggle to understand why a BIA is so important. However, when you think about business continuity as a long-term process, the BIA is the requirements gathering portion of the process. Just like a project manager wouldn’t start executing a project without clear requirements, the same is true for business continuity: a BIA should deliver clear requirements. Specifically, the business impact analysis:
- Provides Confirmation of Business Continuity Program Scope: The BIA identifies the business activities and resources necessary to deliver the organization’s most important products and services. By understanding how the organization delivers its products and services, the BIA process may uncover activities or resources that were not originally in the program’s scope. Also, by understanding activity and resource impacts associated with disruption, the organization can identify which activities and resources need to be performed, regardless of circumstance, which may have an impact on the program’s scope.
- Identifies Legal, Regulatory, and Contractual Obligations: Many organizations do not have a clear, unified understanding of obligations. In fact, it is very rare to see any entity within an organization that has a full grasp of what is required during a disruption, and what the implications are if the organization cannot meet those obligations. The BIA enables the organization to create a thorough understanding of these obligations and to enable the appropriate level of business continuity planning to achieve compliance.
- Provides Clarity on Business Continuity Strategy Spend: One of the most valuable aspects of the BIA is the estimation of impacts tied to downtime. Understanding financial, reputational, contractual, legal/regulatory, operational, and other impacts enable the organization to develop the business case, with appropriate justification, to select, implement, and maintain business continuity strategies. With proper justification, the organization is set-up to identify and implement appropriate capabilities needed to meet recovery objectives – resulting in the appropriate spend.
- Captures Preliminary Plan Content: The BIA process can be used to begin the data collection effort for business continuity plans. When performing the BIA, the organization can begin to collect business continuity plan content, such as existing controls and recovery strategies, team and staffing requirements, internal and external contact information, and other resource-specific information required for the business continuity plan. Once this information is collected, the organization can begin to populate the business continuity plan and present a starting point to those charged with creating and maintain the plans (as opposed to starting with a blank template).
See Also
Business
Business-to-Business (B2B)
Business Application
Business-Driven Development (BDD)
Business-to-Business Gateway
Business-to-Consumer (B2C)
Business Accelerator
Business Activity Monitoring (BAM)
Business Analysis
Business Analytics
Business Application
Business Application Programming Interface (BAPI)
Business Architecture
Business Asset
Business Capability
Business Capability Modeling
Business Ethics
Business Case
Business Centric Methodology (BCM)
Business Continuity Management (BCM)
Business Continuity Plan (BCP)
Business Continuity Planning (BCP)
Business Cycle
Business Diversification
Business Driven Technology
Business Drivers
Business Ecosystem
Business Environment and Internal Control Factors (BEICF)
Business Excellence
Business Expansion
Business Function
Business Function Model
Business IT Alignment
Business Impact Analysis (BIA)
Business Incubator
Business Insurance
Business Integration
Business Intelligence
Business Interruption Insurance
Business Life Cycle
Business Logic
Business Management System (BMS)
Business Model Innovation (BMI)
Business Model for Information Security (BMIS)
Business Motivation Model (BMM)
Business Objects
Business Operations
Business Oriented Architecture (BOA)
Business Mission
Business Vision
Business Model
Business Goals
Business Objective
Corporate Structure
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)
Chief Executive Officer (CEO)
IT Strategy (Information Technology Strategy)
IT Governance
Enterprise Architecture
IT Sourcing (Information Technology Sourcing)
IT Operations (Information Technology Operations)
