Business Life Cycle
The business life cycle is the progression of a business and its phases over time and is most commonly divided into five stages: launch, growth, shake-out, maturity, and decline. The cycle is shown on a graph with the horizontal axis as time, and the vertical axis as dollars or various financial metrics.[1]
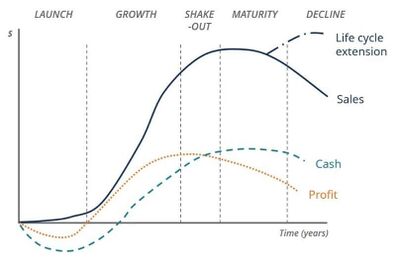
source: Corporate Finance Institute
The Purpose of the Business Life Cycle[2]
Although all businesses are inherently unique, they often follow a similar trajectory. In fact, if you plot a business’ journey from conception to present on a timeline, you’ll usually see five distinct phases. It’s similar to how people grow and mature; the business life cycle shows businesses maturing from infancy through adolescence to adulthood and eventually, old age.
According to the Startup Genome Report, 90 percent of small businesses fail. To be clear, almost all businesses start as small businesses before processing through the stages of business growth. And when a business does fail, it doesn’t usually happen right away.
Though it varies by industry, about 20 percent of businesses fail within one year of launch. Of the 80 percent that remains, 30 percent fail within the second year. Then 50 percent of the remaining businesses fail by the fifth year, and between years five and ten, 70 percent of the remaining businesses fail.
Why? It often boils down to poor planning, preparation, and decision making.
The business life cycle may have originated as an analytics tool, but it’s increasingly used as a business blueprint. Since it outlines the trajectory of a business, entrepreneurs can use the business life cycle to build stronger, healthier businesses.
Navigating The Business Lifecycle[3]
Not all businesses will experience every stage of the business lifecycle, and those that do may not necessarily experience them in chronological order. For example, some businesses may see astronomical growth right after startup, and the founders may decide to cash out right away, jumping straight to that “exit” stage.
For many companies, though, there will be some sort of resemblance to the stages defined above, and awareness may help you anticipate what is coming next and how you can best prepare yourself and your team to maximize your chance of success. Making the right decisions at each stage is another thing altogether, however, and that will require your usual mix of gut instinct and practical business sense.
See Also
Business
Business-to-Business (B2B)
Business Application
Business-Driven Development (BDD)
Business-to-Business Gateway
Business-to-Consumer (B2C)
Business Accelerator
Business Activity Monitoring (BAM)
Business Analysis
Business Analytics
Business Application
Business Application Programming Interface (BAPI)
Business Architecture
Business Asset
Business Capability
Business Capability Modeling
Business Ethics
Business Case
Business Centric Methodology (BCM)
Business Continuity Management (BCM)
Business Continuity Plan (BCP)
Business Continuity Planning (BCP)
Business Cycle
Business Diversification
Business Driven Technology
Business Drivers
Business Ecosystem
Business Environment and Internal Control Factors (BEICF)
Business Excellence
Business Expansion
Business Function
Business Function Model
Business IT Alignment
Business Impact Analysis (BIA)
Business Incubator
Business Insurance
Business Integration
Business Intelligence
Business Interruption Insurance
Business Life Cycle
Business Logic
Business Management System (BMS)
Business Model Innovation (BMI)
Business Model for Information Security (BMIS)
Business Motivation Model (BMM)
Business Objects
Business Operations
Business Oriented Architecture (BOA)
Business Mission
Business Vision
Business Model
Business Goals
Business Objective
Corporate Structure
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)
Chief Executive Officer (CEO)
IT Strategy (Information Technology Strategy)
IT Governance
Enterprise Architecture
IT Sourcing (Information Technology Sourcing)
IT Operations (Information Technology Operations)
